Textile manufacturing is a complex and intricate process that transforms raw fibers into the fabrics we use in our everyday lives. From the cultivation of fibers to the final product, each stage involves a series of carefully orchestrated steps. In this article, we will delve into the various phases of the textile manufacturing process, highlighting the key processes that contribute to the creation of high-quality textiles.
1. Fiber Cultivation:
The journey begins with the cultivation of natural or synthetic fibers. Natural fibers like cotton, wool, and silk are sourced from plants, animals, or insects. Cotton, for instance, is harvested from the fluffy bolls of the cotton plant, while wool is sheared from sheep. On the other hand, synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon are derived from chemical processes involving petroleum-based products.
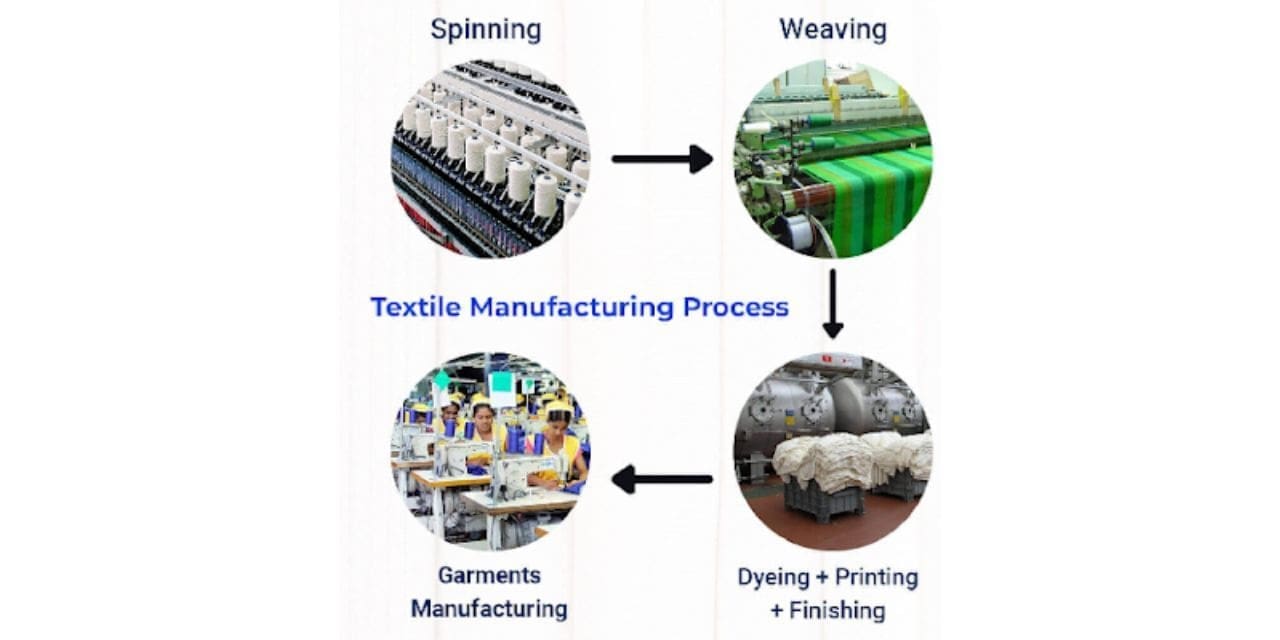
2. Spinning:
Once the fibers are harvested or synthesized, the next step is spinning. This process involves twisting the fibers together to form yarns or threads. In traditional spinning, a spinning wheel is used to draw out and twist the fibers, creating a continuous strand. In modern textile mills, advanced machines like ring or open-end spinners automate this process, producing consistent and high-quality yarns.
3. Yarn Preparation:
After spinning, the yarn undergoes preparation to enhance its quality and usability. This may involve processes such as sizing, where a thin layer of protective material is applied to strengthen the yarn, or twisting multiple yarns together to create a thicker, more robust strand. Yarn preparation sets the stage for the subsequent weaving or knitting processes.
4. Weaving or Knitting:
Weaving and knitting are the two primary methods used to turn yarns into fabrics. In weaving, yarns are interlaced at right angles to create a woven fabric. This process is commonly employed for materials like cotton and wool. Knitting, on the other hand, involves interlocking loops of yarn to form a flexible fabric, making it suitable for stretchy materials like jersey and sweaters.
5. Dyeing and Printing:
Once the fabric is woven or knitted, it is often treated with dyes or pigments to add color and patterns. Dyeing can occur at various stages of production, either when the yarn is still in its raw form or after the fabric is woven or knitted. Printing involves applying colors or patterns directly onto the fabric’s surface using techniques like screen printing or rotary printing.
6. Finishing:
After dyeing or printing, the fabric undergoes finishing processes to improve its appearance, texture, and durability. This may include treatments such as calendering to smooth the surface, singing to remove any loose fibers, or coating to add water resistance. Finishing plays a crucial role in achieving the desired characteristics of the final textile product.
7. Quality Control:
Throughout the entire manufacturing process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the textiles meet specific standards. This involves inspecting the fibers, yarns, and fabrics at various stages to identify and rectify any defects. Quality control is essential for producing textiles that meet customer expectations in terms of appearance, strength, and performance.
8. Packaging and Distribution:
The final step in the textile manufacturing process involves packaging the finished products for distribution. Textiles may be rolled onto bolts, folded, or packaged in various forms depending on their intended use and market requirements. Efficient logistics and distribution networks ensure that the textiles reach their destination in optimal condition.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the textile manufacturing process is an intricate journey that transforms raw fibers into the fabrics we use in our daily lives. From fiber cultivation to packaging and distribution, each stage requires precision and expertise to produce high-quality textiles. The interplay of traditional craftsmanship & newsblare.com ensures that the textiles we enjoy are not only aesthetically pleasing but also durable and functional. Next time you wrap yourself in a cozy blanket or put on your favorite outfit, take a moment to appreciate the intricate journey of unraveling the thread that led to the creation of that textile.