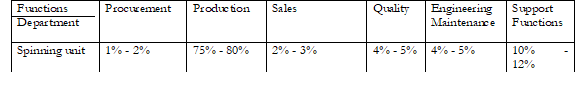Spinning Mills
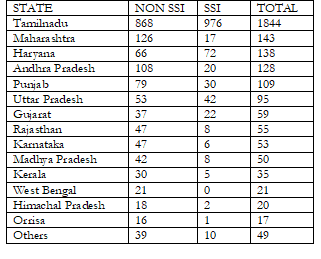
At end of March 2008, India had around 2,816 spinning mills including 1,219 in the small-scale industries (SSI) sector. These mills had an installed capacity of 34.41 million spindles (including 4.17 million in the SSI sector), and a workforce of 0.625 million (including 0.05 million in the SSI sector).Tamil Nadu (TN) has the highest number of spinning units and accounts for 65% of the total number of spinning units in the country
State-wise number of spinning mills
Source: Ministry of Textiles, IMaCS Analysis
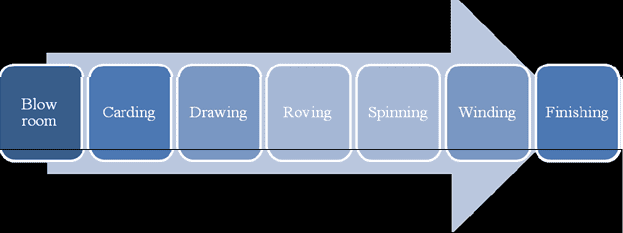
- Production processes involved in spinning
Common industrial spinning techniques include ring spinning, open-end (rotor) spinning, and air-jetspinning. The process description of a typical ring spinning process is depicted below.
Production processes in spinning
Blow room operations: The blow room machinery performs the function of opening pressed bales of cotton and cleaning the cotton of impurities. Trash and foreign matter is extracted from the cotton with the least amount of lint loss. Blow room line consists of opening, cleaning, mixing and lap making machine. In order to produce uniform quality of yarn and also to reduce the cotton cost of yarn while achieving the desired level quality, mixing of two or more types of cotton is carried out in the blow room. The loose cotton passed through the blow room machinery is converted into regular sheets called laps.
Carding: The material received from Blow room is processed on the Carding machines which produce a thin sheet of uniform thickness that is then condensed to form a thick, continuous, untwisted strand called sliver. This process also removes the remaining impurities from the cotton.
Drawing: The fibers in the carded sliver are placed in a haphazard fashion and lack uniformity. The carded slivers are processed on the drawing frame; they are made uniform in thickness by the doubling process. The fibers get drawn parallel to the axis of the sliver by the drafting process.
Roving: Slivers are to be thinned out to the level required for the yarn to be spun. This process of attenuating the slivers is done in several steps on Speed Frames. While converting slivers into roving, a small amount of twist is also inserted so that the roving can withstand the winding and the unwinding operations.
Spinning: The roving bobbins are taken to the ring frames where it is drafted (extended) to the extent of desired level (i.e. count). The spindle along with the ring traveller mounted on a ring imparts the requisite amount of twist into the yarn. The yarn is wound on bobbins and taken to post spinning operations.
Winding: The yarn is wound over paper cones to make final packages after passing through electronic yarn cleaners for removal of any defects. The ends are ‘spliced’ to produce knot-less yarns.
Finishing: Further operations on the yarn, such as Bleaching, Dyeing, and Packaging will depend on the intended usage of the yarn.
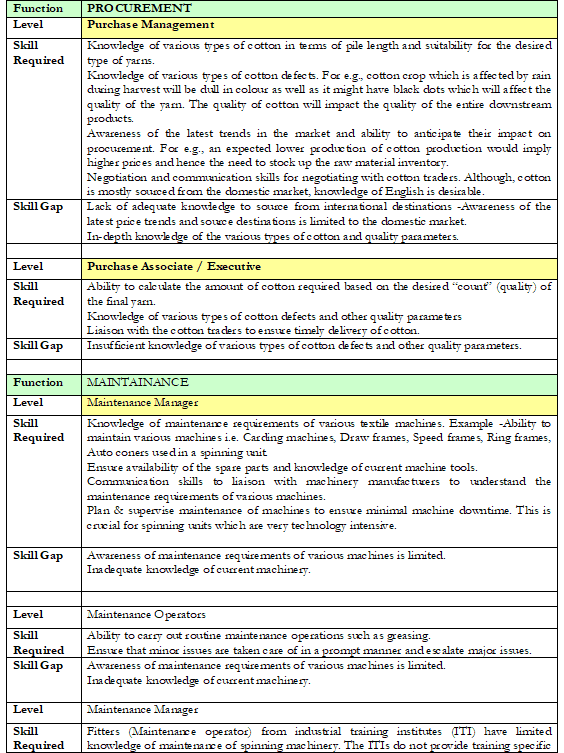
SKILL REQUIREMENTS AND SKILL GAPS IN SPINNING
FUNCTION : PRODUCTION
LEVEL : Production Manager / Shift In charge
SKILL REQUIRED
Ability to oversee plant operations
Problem solving skills, good communication skills to manage shop floor workers who are mostly minimally educated.
Technical competence- Very strong understanding of all aspects of the spinning process. Technical knowledge is a must as spinning sector is technology intensive in nature.
Process improvement skills – waste control, finding solutions to maintenance and engineering related problems as most of the units do not have a dedicated R&D for process improvement. Yarns are a commodity product which leads to thin margins for the producers. Cost reduction through above mentioned measures is a must to improve profitability.
SKILL GAPS
Inadequate cross-functional knowledge especially of maintenance.
Inadequate practical knowledge of tools
Insufficient soft skills to manage shop floor people.
Awareness of modern production methods and machines is limited.
LEVEL : Supervisor
SKILL REQUIRED
In-depth knowledge of production process. Knowledge about the various spinning machines used across the shop floor.
Man-management skills to manage shop floor workers who are mostly minimally educated.
Ability to train operators to man the spinning machines.
Awareness of quality requirements of the yarn across various stages of production.
Monitor cleaning and maintenance schedule of the spinning machinery.
SKILL GAPS
Lack of man-management skills to manage shop floor personnel.
The supervisors typically have work experience in particular processes of the spinning mill as operator and do not have a formal training/education of other processes.
Awareness of modern spinning machines is limited.
LEVEL : Operator
SKILL REQUIRED
Operating knowledge of the spinning machines.
Ability to ensure that machine stoppage time in minimal
Monitor spinning operation as regards the availability of sliver/bundles/lap as input to respective stages of the spindling operation
Should be able to read gauges, dials, or other indicators to make sure a machine is working properly.
Ability to work on different machines. For e.g. a spinning operator should be able to work on carding, roving and spinning machines.
Discipline at shop floor, punctuality and regular attendance at workplace.
Adherence to cleaning and machine maintenance schedule. Understanding of support to be provided for maintenance of various textile machines
Ability to comply with quality norms.
SKILL GAPS
Knowledge/ Skill confined to single or few machines
Lack of knowledge of compliance to quality
Inadequate ability to multitask between different types of machines.
FUNCTION : QUALITY
LEVEL : Quality Control Supervisor / Manager
SKILL REQUIRED
Understand the quality requirements of the yarn in terms of “count”, breakage during weaving etc.
Understanding of the quality parameters across the various stages of assembly line.
Knowledge of the cause of various defects. For example, the Supervisory should know that a particular defect (like black dots) in the yarn is due to improper quality of cotton or particular manufacturing process.
SKILL GAPS
Inadequate ability to translate buyer requirements to quality parameters
Lack of knowledge of cause-effect relationships for various defects (such as breakage of threads).
LEVEL : Quality Control Executive
SKILL REQUIRED
Understanding of the quality parameters.
Ensure that the quality parameters are adhered to by diligently checking the product. For e.g. Yarn marked as count 40 should not be 38/39 which will significantly affect the fabric manufacturers.
Act promptly and liaison with production to minimize the quality issues.
SKILL GAPS
Inadequate understanding of quality parameters.
FUNCTION : SALES
LEVEL : Sales Manager
SKILL REQUIRED
Detailed product knowledge in terms of type of fibre and other technical parameters.
Good negotiation skills are a must as the yarn market is very cost sensitive. Minor quality issues tend to result in high discounts.
Good communication skills to interact with the team as well as with the important clients. Knowledge of English is important in case of international clients.
SKILL GAPS
Negotiation and communication skills. Also, South-based spinning mills require people with knowledge of Hindi which are difficult to find.
LEVEL : Sales Executives
SKILL REQUIRED
Awareness of competitor actions and provide feedback to the management.
Understanding of customer requirements in terms of quality of yarn.
Good communication skills to interact with the team as well as with the important clients.
SKILL GAPS
Negotiation and communication skills. Also, South-based spinning mills require people with knowledge of Hindi which are difficult to find.
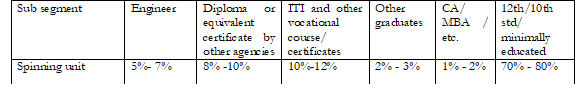
Functional distribution of human resource across key sectors.
Distribution of human resource by education level
Reference:
- ICRA Management Consulting Services Limited (IMaCS).
- www.nsdcindia.org.