Synopsis
• In April 2023, banks’ outstanding credit to non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) rose by 29.2% (y-o-y) to
reach Rs.13.5 lakh crore. The growth has remained robust due to high growth in the NBFC asset book and as additional borrowings moved to banks due to yield differentials and lower borrowingss in the overseas market.
• The Mutual Fund (MF) debt exposure to NBFCs rose marginally by 0.2% y-o-y to Rs.1.6 lakh crore. The share
of MFs has been on a broadly reducing trend for the last several quarters.
• MFs’ debt exposure to NBFCs has increased to 12% of Banks’ exposure to NBFCs in April 2023 from 10.97%
in March 2023 and 10.8% in February 2023. This figure was 16.6% in March 2022 and 15% in April 2022.
Banks O/s Credit to NBFCs Continues its Robust Growth, MFs Pare Exposure
Banks’ outstanding credit to NBFCs rose by Rs.2.6 lakh crore over the last 12 months. Meanwhile, MF debt exposure
(CPs and Corporate Debt) to NBFCs increased marginally by 0.2% y-o-y to Rs.1.60 lakh crore in April 2023, while increasing sequentially by 9.8% from March 2023 levels.
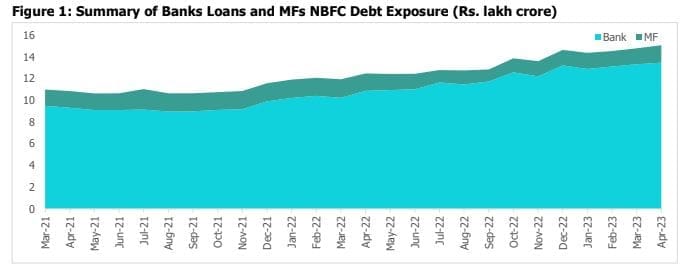
The data in Figure 1 does not include liquidity made available to NBFCs by banks via the securitization route (direct
assignment & pass-through certificates) and investments made by banks in the NBFCs’ capital market issuances.
Liquidity availed by NBFCs including HFCs through the securitisation route crossed approximately Rs 1.7 lakh crore
in FY23.
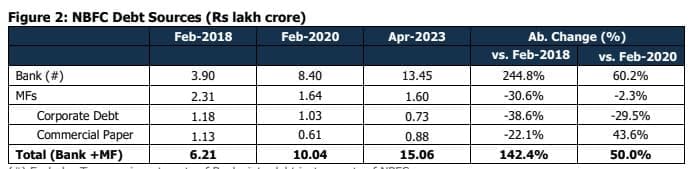
Compared to February 2018 numbers, absolute bank lending to NBFCs has more than tripled, while MF exposure
has broadly reduced by over a third over the last five years. If April 2023 data is compared with February 2020
numbers, bank borrowings have increased by 60.2%, MF Corporate Debt exposure has reduced by 29.5%, and MF
CP exposure has increased by 43.6%.
MFs debt exposure to NBFCs has increased to 12% of Banks’ exposure to NBFCs in April 2023 from 10.97% in
March 2023 and 10.8% in February 2023. This figure was 11.5% in January 2023 and 16.6% in March 2022.
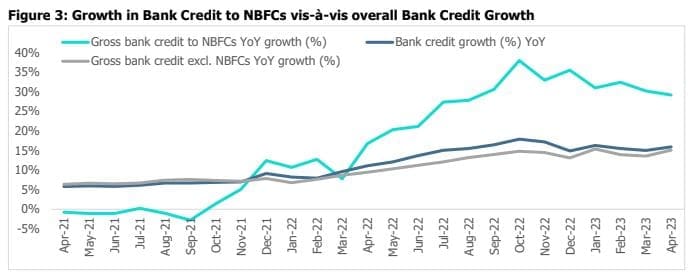
The latter part of FY22 saw healthy growth in bank credit to NBFCs, which has continued its upward trajectory into
FY23. This growth can be attributed to several factors, including the base effect, the improved financial position
and growth visibility of NBFCs, yield differentials and lower borrowings in the overseas market. As of April 2023,
lending to NBFCs accounted for 7.9% of the incremental lending of aggregate credit.
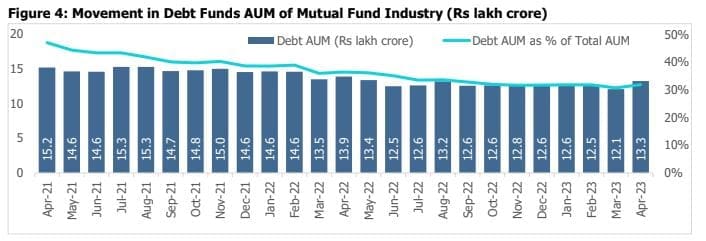
The debt assets under management (AUM) of mutual funds decreased 4.6% y-o-y to Rs.13.3 lakh crore in April
2023. This decrease can be attributed to the popularity of equity funds, fixed-term plans (FMP) losing popularity,
and alternate investment avenues, meanwhile, the decline has slowed as liquid funds have witnessed inflows.
Investment in corporate debt of NBFCs fell by 9.2% y-o-y to Rs.0.73 lakh crore in April 2023. The percentage share
of total corporate debt to NBFCs too declined to 4.2% in April 2023 from 4.8% in April 2022. On the other hand,
the numbers have increased sequentially by 7.7% compared to March 2023 (Rs.0.67 lakh crore).
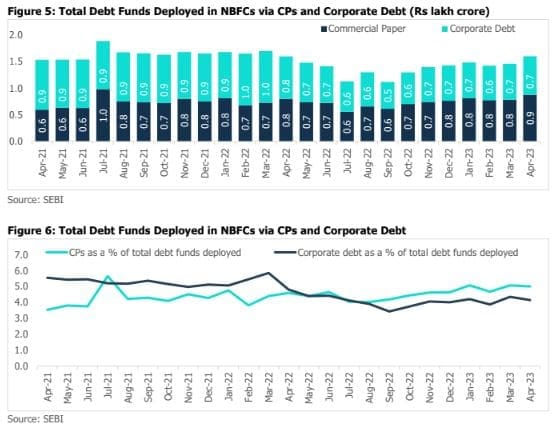
The outstanding investments in CPs of NBFCs increased by 9.5% y-o-y to Rs.0.88 lakh crore in April 2023. CPs
(less than 90 days) rose by 12.9% y-o-y to Rs.0.59 lakh crore in April 2023, CPs (90 days to 182 days) fell by nearly
a third to Rs.0.09 lakh crore, and the more than 6 months (CPs) increased by nearly 80% to Rs.0.18 lakh crore in
the reporting period. The percentage share of funds deployed by MFs in CPs of NBFCs in April 2023 stood at 5.01%
(compared with 4.57% in April 2022).
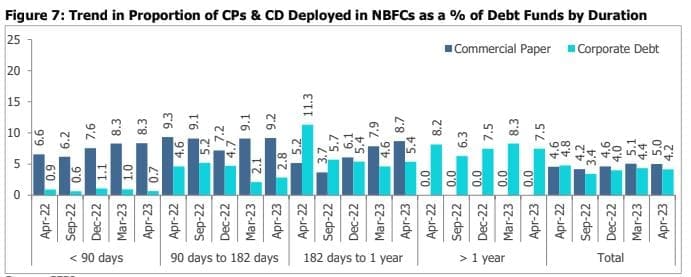
The proportion of CPs (less than 90 days) deployed in NBFCs as a percentage reached 8.34% in April 2023 as
compared to 6.58% over a year ago period, the percentage of CPs (90 days to 182 days) fell to 9.18% from 9.34%
over a year ago, and CPs (greater than six months) percentage too grew to 8.7% in April 2023 as compared to
45.18% over a year-ago period.
Conclusion
The credit exposure of the banks to NBFCs stood at Rs 13.5 lakh crore in April 2023 2 as NBFCs have witnessed growth in the post-pandemic period, yields differentials and lower international borrowings. Additionally, NBFC exposure as a percentage of aggregate credit has moved from 9.1% in April 2022 to 9.7% in April 2023. Hence certain banks may face difficulties in extending further credit to the NBFC sector as they move closer to the sectoral exposure norms. Meanwhile, MFs’ share has declined for the last several quarters as they primarily maintain their exposure to NBFCs via market instruments. Further as and when banks fully transmit the rate hikes to their borrowers, market borrowing by NBFCs may increase as the spread between bank rates and market yields soften.
Meanwhile, given the general credit risk aversion of MFs, the exposure to NBFCs, especially those rated below the highest levels is not likely to increase meaningfully. Hence, the NBFC’s dependence on the banking sector for funding is likely to remain very high.

