It is expected that polyester will cover more than 60% share of the total fibre demand on a global level by 2030, while cotton will account for about 1/4th Share. Changing consumer lifestyles cantered on affordability, functionality, and availability is driving the demand for MMF Consumption. This article talks about the current status of the MMF Industry and what opportunities it brings for the Indian Players.
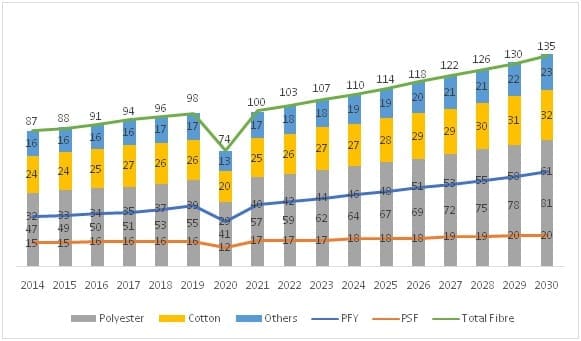
MMF sector is growing significantly worldwide
The Manmade Fibre (MMF) segment accounts for 70% share in the global fibre consumption with the majority of share held by polyester fibre. The global fibre consumption has increased from 87 mn. tons in 2014 to 103 mn, tons in 2022. Polyester has replaced cotton to become the largest and the fastest growing category in the world with current global consumption of 57 mn. tons. The demand for manmade fibre is growing significantly across the world. There are several reasons behind this trend. Low cost, the demand-supply gap in cotton, and versatility in design and application are some of the key reasons. Realizing the potential of the synthetic Industry, the government of India has also taken the initiative to promote synthetic textile manufacturing in India and launched dedicated schemes like PLI and MITRA.
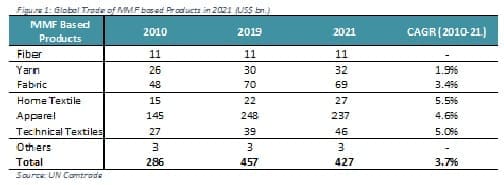
MMF products accounts for approximately half of the global trade
The global trade of textile and apparel stood at US$ 871 billion in 2021 with a significant increase of 22% post covid. Approximately, 49% i.e. US$ 427 bn. of the global trade comes from man-made fibers and is growing at a CAGR of 3.7% since 2010. In 2021, MMF based apparel stood at US$ 237 bn. growing at a CAGR of 4.6% while cotton based apparel stood at US$ 207 bn. MMF based fabrics being the second largest category stood at US$ 69 bn. growing at a CAGR of 3.4% during the same period.
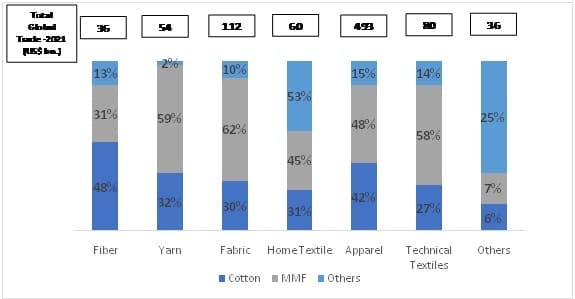
MMF dominates the global trade in yarn fabric, apparels and technical textiles categories
Currently, MMF sector dominates the global trade in yarn(59%), fabric(62%), apparel(48%) and technical textile(58%) category whereas cotton dominates in the fibre(48%) category.
MMF accounts for 48% of the global apparel trade in 2021
In the near future, while there is significant opportunity across all fibre types and products, However, MMF based apparel products are expected to lead the future. Out of the top 10 traded apparel categories, Trousers, Sweaters, and Dresses are the major MMF based categories with 38%, 41% and 69% MMF share respectively. Other major MMF categories are Jackets, Overcoats, Hosiery, and Brassieres. A total of US$ 237 bn. was traded globally in MMF category which accounts for 48% in the global trade, 6% higher than the cotton-based apparel trade. In 2021, Woven apparel has 4% more trade in MMF based categories than Knitted Apparel.
Figure 4: Top 10 apparel categories traded globally (values in US$ bn.)
| Sr. no. | Category | Cotton | MMF | Others | Trade (US$ Bn.) | Share | MMF Value | MMF Share |
| 1 | Trousers | 61% | 38% | 1% | 105 | 21% | 40 | 17% |
| 2 | Sweaters | 46% | 41% | 13% | 66 | 13% | 27 | 11% |
| 3 | T-Shirts | 70% | 25% | 4% | 48 | 10% | 12 | 5% |
| 4 | Dresses | 30% | 69% | 1% | 30 | 6% | 21 | 9% |
| 5 | Jackets | 38% | 51% | 11% | 26 | 5% | 13 | 6% |
| 6 | Overcoats | 16% | 60% | 24% | 18 | 4% | 11 | 5% |
| 7 | Hosiery | 3% | 97% | 0% | 14 | 3% | 14 | 6% |
| 8 | Blouses | 44% | 43% | 13% | 13 | 3% | 6 | 2% |
| 9 | Brassieres | 0% | 100% | 0% | 12 | 2% | 12 | 5% |
| 10 | Babies Garments | 79% | 16% | 5% | 11 | 2% | 2 | 1% |
| 11 | Others | 29% | 53% | 17% | 152 | 31% | 81 | 34% |
| Total | 42% | 48% | 9% | 493 | 100% | 237 | 100% |
Source: UN Comtrade
Key Factors driving the growth of the synthetic textiles

Changing Consumer lifestyle is driving the growth of the MMF sector
The impressive growth and volume of polyester fibre consumption are driven by the trends in the global market. Other synthetic fibers gaining importance are recycled nylon, lyocell, and viscose. However, polyester remains the dominant fibre in the synthetic category. The changes in the consumer lifestyle and attitude drive the trends in the end products.The demand is rising considering the following premises:
- Increased emphasis on fitness: As more and more people are opting for sports and physical exercises realizing the need to prioritize health, especially after the pandemic. The increased fitness focus eventually leads to an increase in demand for activewear that provides comfort along with performance.
- Fashion Cycles are very short:Brands frequently introduce new products and styles in the market. The fast fashion industry has become majorly dependent on synthetic fibres, such as polyester, which have become the backbone of their business model.
- Good quality, affordable prices: Prices of cotton have been soaring in the past half-decade and have escalated to more than INR 75k / Candy. To counter the high-priced fibre, polyester overtook as the most in-demand fibre, nowadays polyester costs half as much per kilo as cotton and has the capability of providing functional properties such as stretch, durability, and easy maintenance.
- Rising demand of Industrial textiles: Most technical textiles like Tyre cords, Seatbelt webbings, Upholstery material, Conveyor belting fabric, etc.can only be produced using man-made fibres. A drastic increase in demand for these industrial-use fabrics is pushing to increase man-made fibre demand.

Cotton has Limitation for Future Growth
While the usability of synthetic fibres may be pushing their demand, there are other factors like less-desirable qualities of cotton which will drive the consumer to rely more on man-made fibres in the times to come. A huge fertile land mass comprising black soil is required to produce cotton fibre, while the cotton demand has always been high, the fibre production has been unable to keep up with it. Moreover, cotton production also requires 20,000 Litres of water to produce 1Kg fibre and many more pesticides detrimental to the soil causing a major sustainability issue. Also, the chemical and physical properties of cotton have made its application area limited and unfit for various products today.
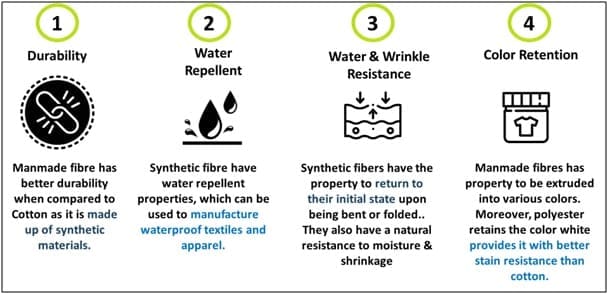
Manmade fibres are versatile in nature
Manmade fibres have various properties which make them the most in-demand fibres today, they are more durable than cotton and can withstand rough usage, especially in case of sports activity and industrial uses. Manmade fibres are also water repellent and can be used in making waterproof textile and apparel. Sweat-proof textile especially used in sports activities majorly uses synthetic fibres. Synthetic fibres are easy to maintain and require less care, MMF based fabrics are wrinkle-free and easily return to their initial stage upon being bent or folded. They also have a natural resistance to moisture and shrinkage. Synthetic fibres can be dyed easily as per the required shade Moreover, polyester retains the colour white and provides stain resistance better than cotton does.
Growth in Synthetic fibres
Rigorous material research and innovation in synthetic fibres are continuously widening their application areas.Following are some of the major developments in synthetic fibres:
Figure 8: Growth prospect of Synthetic fibres
| Developments | Feature | Application area |
| Hollow fiber | Light weight, superior resilience, thermoregulatory | Premium pillows, cushions and quilts |
| Micro fiber | Fast dyeing, ultra-soft touch | Sweater, garments, business suit, home textiles |
| Inherently stretchable fibre | Substitute for Spandex | Sportswear, apparel |
| Ecofriendly flame-retardant fiber | Slow combustion and self-extinguishment | Home textiles, Kids wear, work wear |
| UV retardant fibre | Cooling effect in heating environment | Casual wear, sportswear, swimwear, uniform |
| Anti-microbial fiber | Ecofriendly and permanent antimicrobial effect | Home textiles, kids wear, inner wear, gloves, towels |
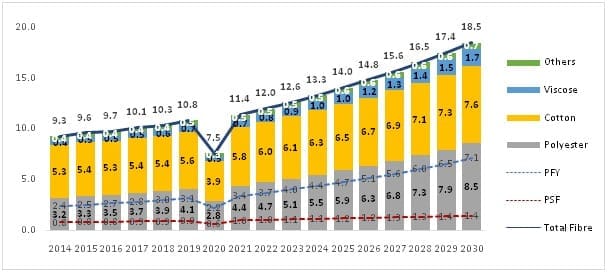
Status of MMF textiles in India
India has traditionally been known as a cotton-producing country, in fact, India is the largest producer of cotton yarn in the world with US$ 3 billion worth of cotton yarn exported in 2019-20. India’s current spindle capacity is 56.6 million spindles which are 2nd largest in the world, most of which are dedicated to producing cotton or cotton blended yarns only. Nevertheless, the demand for synthetic fibre is on the rise in India day by day. It is estimated that polyester consumption in India will double itself and reach 8.5 mn. tons by 2030 from the current estimated consumption of 4.4 mn. tons, growing at a CAGR of 8%. The growth in India is mainly driven by the growing domestic and exports in T&A market.
Figure 9: India’s Fibre Consumption (Million tons)
Source: PCI Fibres, CCI, Wazir Analysis
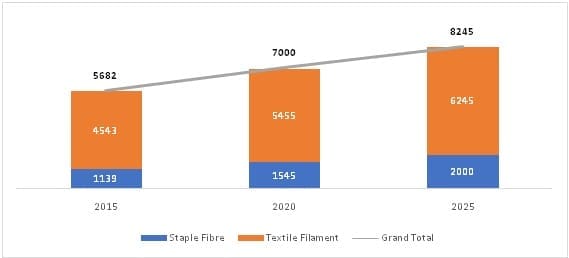
India’s installed polyester capacity is growing significantly
Currently, India has an installed polyester capacity of more than 7000 KTPA which is estimated to grow annually by CAGR 3.3% and reach 8245 mn. tons in the next three years. the polyester capacity will continue to rise even to match the fast-growing demand for the polyester fibre.
India Exported US$ 4.7 billion worth of MMF based apparel in 2021
Exports of MMF based textile and apparel have increased from US$ 6.8 bn. in 2010 to US$ 11.6bn. in2021, indicating a growth of 5%. Exports of technical textiles, Apparel, and Hometextiles witnessed a significant growth of 13%, 8% and 6% respectively while exports of fabric showed a decline of 2% during the same period. In the Indian MMF textile and apparel exports, apparel contributes to a maximumshare of 41% followed by technical textiles and fabrics with 14% share each.
Major markets for India MMF based textile and apparel exports are UAE, USA and UK.
| MMF Based Products | 2010 | 2019 | 2021 | CAGR (2010-2021) |
| Fiber | 0.5 | 1 | 0.6 | 2% |
| Yarn | 1.4 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 4% |
| Fabric | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.6 | -2% |
| Home Textile | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 6% |
| Apparel | 2.1 | 5.9 | 4.7 | 8% |
| Technical Textiles | 0.4 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 13% |
| Others | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | -2% |
| Total | 6.8 | 12.3 | 11.6 | 5.0% |
Source: UN Comtrade
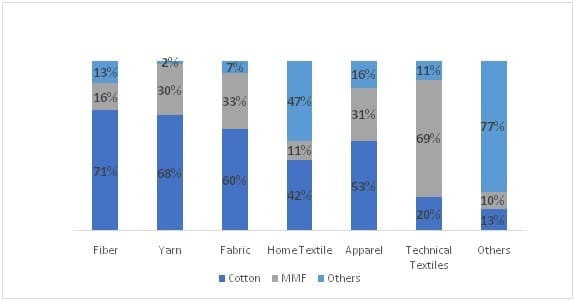
Cotton has majority of share in Major T&A category while MMF has higher growth
On the fibre level, MMF has a 28% share in India’s T&A exports while the majority of share is taken by cotton products only. In the present scenario, technical textile is the only category where MMF dominates the cotton products with a 69% share.
Currently, MMF sector dominates the global trade in yarn(59%), fabric(62%), apparel(48%) and technical textile(58%) category whereas cotton dominates in the fibre(48%) category.
India is gaining strength in top MMF apparel commodities traded globally
In 2021, India’s share in the top MMF traded category globally was only 2%. However, India has shown significant growth of CAGR 8% in the MMF based apparel Category since 2010. India’s presence is still insignificant in the majority of MMF apparel commodities except for Dresses and Blouses where India has a reasonable share of 12% and 11% respectively. Going forward India can focus on consolidating these categories however, diversification to new categories is a must. Categories like Trousers, Sweaters, Jackets, Brassieres, and Overcoats are some of the major categories where India can focus expansion in order to increase its share in the global MMF apparel market.
Figure 13: India’s Share in top MMF apparel Categories traded globally (Values in US$ billion)
| Sr. no. | Row Labels | Global Trade | China | Bangladesh | Viet Nam | India | India’s Share | India’s Growth (2010-21) |
| 1 | Trousers | 19.7 | 12.0 | 2.4 | 4.3 | 0.9 | 4% | 14% |
| 2 | Sweaters | 15.0 | 11.1 | 2.2 | 1.5 | 0.05 | 0.3% | 11% |
| 3 | Dresses | 9.2 | 6.9 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 12% | 13% |
| 4 | Hosiery | 8.7 | 6.3 | 0.03 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 2% | 20% |
| 5 | Jackets | 6.7 | 8.0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 3% | 10% |
| 6 | Brassieres | 6.2 | 4.4 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 1% | 6% |
| 7 | Overcoats | 4.5 | 3.2 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.04 | 1% | 4% |
| 8 | Gloves | 3.4 | 2.9 | 0.04 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 2% | 10% |
| 9 | Blouses | 3.2 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 11% | 3% |
| 10 | Swimwear | 3.0 | 2.0 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.2% | -7% |
| Others | 157 | 34 | 3 | 7 | 2 | |||
| Total | 237 | 92 | 10 | 17 | 5 | 2% | 8% |
Source: UN Comtrade
In 2021, India Imported US$ 4.8 Billion worth of MMF based T&A commodities.
MMF has a significant share in India’s T&A imports. In 2021, India imported US$ 4.8 billion worth of MMF based T&A commodities grew at a CAGR of 11% since 2010. Yarns are the most imported category with 34% share followed by fabric and technical textiles with 20% and 17% share respectively. India imported only US$ 600 million worth of MMF based apparel. However, apparel imports are growing significantly at CAGR 27%. This also presents a great import substitution opportunity for Indian manufacturers. Installing MMF capacities in fabrics and apparel will not only generate higher revenues from the export market but also establish a market in the growing domestic market of India.
Figure 14: India’s MMF imports in Major T&A Categories (Values in US$ bn.)
| MMF Based Products | 2009-10 | 2019-20 | 2021-22 | CAGR (2010-22) | Share |
| Fibre | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 10% | 10% |
| Yarn | 0.6 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 9% | 34% |
| Fabric | 0.2 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 13% | 20% |
| Home Textiles | 0.04 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 7% | 2% |
| Apparel | 0.03 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 27% | 12% |
| Technical Textiles | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 8% | 17% |
| Others | 0.03 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 20% | 5% |
| Total | 1.4 | 3.9 | 4.8 | 11% |
Source: DGCIS
China, Vietnam, Bangladesh and Thailand were the top suppliers for MMF based textiles and Apparel to India.
Invest Opportunity in Synthetic Textiles for India is Huge
With the growing textile and apparel market of India and improving export competitiveness, there are significant opportunities across all fiber types and products. However, MMF based textile products are expected to lead the demand globally. To keep up with the current needs, Indian companies need to invest and develop capabilities in MMF textile and apparel products to tap the value-added segment. Performance-based MMF fabrics, which are currently not being manufactured in India sufficiently offers huge potential for future investments. Potential investment opportunities in Synthetic textiles are discussed below:
- Investment in Better Infrastructure and completing the Value Chain
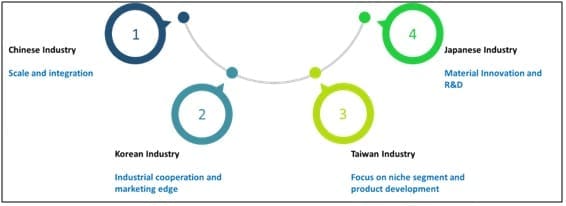
India needs to build large capacities in the MMF sector which are capable of running efficiently while producing high-quality low-cost products. Fabric manufacturing, processing, and garmenting are the most attractive opportunity in the MMF sector. Investment in fabric manufacturing will fix the weak-link in the manmade fibre textile value chain, the manufacturers need to build capacities in 100% MMF based value-added products in which India has a very low production capacity. Processing is also very important in order to produce MMF based value-added products. India needs to produce high quality processed fabrics which are majorly imported in India. Garmenting has low entry barrier and can be started with low investment compared to fabric manufacturing and processing. There is huge demand in garmenting from global brands like H&M, Zara who are exploring sourcing options other than China to reduce dependency on China. Global MMF based textile manufacturing is largely dominated by countries like Korea, Taiwan, Japan and China. Each one of these has developed its own USP to grow and occupy a distinct position in the industry. Indian textile industry can learn a lot from the following strategies of these global leaders:
Figure 15: Key Takeaways from Global Leaders
- US$ 4.7 Billion worth of Import Substitution Opportunity
India imported synthetic fabric worth US$ 1bn., Yarn worth 1.6 bn. apparel worth 0.6 bn. and technical textile worth 0.8 bn. in year 2021. India nearly has no presence in high-end segment and hence the majority of the high-quality MMF products are being imported by India from countries like China, Korea & Taiwan. Production of such categories should be promoted in India.
- Unlocking the Export potential through product diversification and Consolidation
Global and Indian trade data analysis shows that India needs to increase its Market share in the synthetic fabric & apparel trade. The main focus needs to be given tothe manufacturing of top traded and fastest growing fabric and garment categories. India needs to consolidate on manufacturing Dresses and blouses while diversifying in new MMF categories such as Trousers, Sweater, Jackets, Brassieres and Overcoats.
Figure 16: Export Opportunity for India in MMF Sector
| Category | Consolidate | Expand |
| Apparel | Blouses, Dresses | Trousers, Sweaters, Jackets, Brassieres, Overcoats |
| Textile | Cotton Synthetic Blended Fabrics | 100% Synthetic Value-added fabrics both knitted and woven |
- Government visions to make India a Major Synthetic Textile Manufacturing Hub
The Indian government is actively supporting the growth of MMF sector in India. In order to make India a major synthetic textile manufacturing hub, the Indian govt. has introduced multiple policies namely Production Linked Incentive (PLI), Mega Investment Textile Parks (MITRA) and National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM).
PLI scheme, which was recently launched to promote synthetic textile and technical textiles with an outlay of Rs. 10,683 crores has seen active participation from manufacturers across India. A total of 61 companies have been shortlisted for the grant under the PLI scheme. Realizing the active participation, the government has also planned to launch a PLI-2 scheme soon which will further promote the investment in the T&A sector
Seven MITRA parks across the country shall be allocated to states based on bids. The MITRA parks will be fully integrated from fibre to final product and the government plans to incentivise man-made fibre-based manufacturing. The government has also announced National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM)with a view to positioning the country as a global leader in Technical Textiles. The mission has 4 components – Research Innovation & Development, Promotion, and Market Development, Export Promotion and Education, Training and Skill Development.
- Brands are increasing usage of Recycled Synthetic fibres to address the Sustainability Issue
There are lot of concerns around using synthetic textiles as it is not eco-friendly. However, it is not entirely true, there are a lot of benefits of using synthetic materials which makes it a better choice compared to Cotton. Producing polyester may require more energy but it consumes significantly less water than producing the same amount of cotton. Synthetic materials are 100% recyclable and global brands like H&M, Nike, etc. are using more and more recyclable synthetics in their products. Being a chemically driven product, polyester undergoes continuous improvements and innovation to make it a better and more sustainable alternative. Polyester fibres are now starting to be produced from post-consumer and post-industrial recycled materials. Companies are also working hard to invent enzymes that are capable of completely decomposing synthetic material without leaving any traces. A recently found enzyme called polyester hydrolase (PHL7), was able to decompose polyethylene terephthalate (PET) by 90% in less than 16 hours. It is true that road to sustainability is hard and expensive, however, recent developments suggest that soon, synthetic textiles will become completely Sustainable and environment friendly textiles.
- Challenges for India that needs to be countered in order to become a leader in MMF Industry
In 2018, the Government hiked the import duty of synthetic textiles & apparel to boost the manufacturing of the same in India. Contrasting to the expectations the initiative didn’t bring any big changes in the import trends of the industry, this creates a sense of worry about the Industry’s growth expectations from the recently launched government schemes. Despite the tremendous opportunities available in the synthetic textiles sector, Indian players need to master the know-how of processes involved in synthetic textiles manufacturing. The major problem existing with the Indian manufacturers is the lack of scale, poor integration, lack of trained manpower, weak coordination across the value chain, lack of automation technologies, and lesser focus on research and innovation activities. However, all these shortcomings can be rectified by taking proper interventions such as tie-ups with global manufacturers for technical know-how, investing strongly in training manpower, reworking SOPs, using automation technologies where ever possible, opting for an expert consultation on critical areas such as reengineering factories, and tapping new markets, taking a cluster approach to attain scale and lastly a strong action plan for the post covid scenario.
Way forward
Polyester is the fibre of the future and global textile players have already started aligning their businesses accordingly while India remains largely cotton-focused. The opportunities in the MMF sector are huge for India and with the right approach, these opportunities can be successfully converted into profitable businesses. India is in the right spot today to bring in mega investments in the MMF value chain as global buyers are looking for alternate bases (other than China) and the Indian government is providing tremendous support for investment through various schemes and actively working towards finalization of FTA with key markets. Many players have already done capacity expansion in the MMF sector and many others are planning to do so, Hence, it can be expected that India may enhance its export competitiveness and become a major synthetic textiles manufacturer shortly.

