Introduction:
The rise of new digital industrial technology, known as Industry 4.0, is a transformation that makes it possible to gather and analyze data across machines, enabling faster, more flexible, and more efficient processes to produce higher-quality goods at reduced costs.
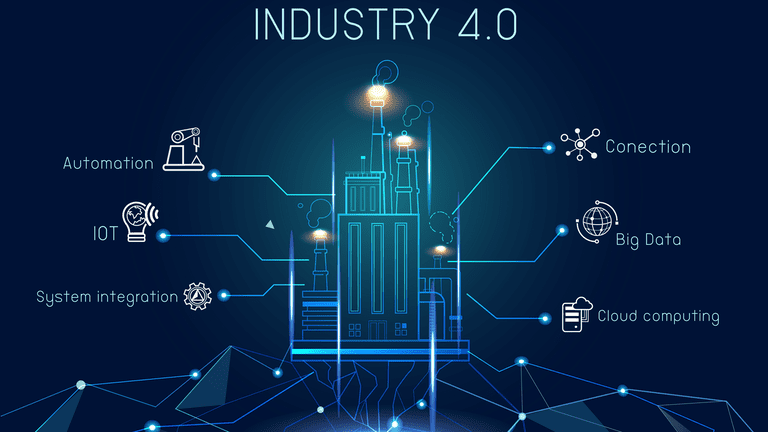
Industry 4.0 is used interchangeably with the fourth industrial revolution and represents a new stage in the organization and control of the industrial value chain. Industry 4.0 has been defined as “a name for the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies, including cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud computing and cognitive computing and creating the smart factory”.
Industrial Revolution:

- The first industrial revolution, thanks to invention of steam machines, the usage of water and all sorts of other machines, led to the industrial transformation of society with mechanization of manufacturing.
- The second industrial revolution is typically seen as the period where electricity and new manufacturing inventions which led to the area of mass production and to some extent to automation.
- The third industrial revolution had everything to do with the rise of computers, computer networks, and the rise of robotics in manufacturing, connectivity. And the birth of the Internet was the biggest game changer with far more automation.
- In the fourth industrial revolution, the bridging of digital and physical environments is happening with automation and optimization in innovative ways that leads to ample opportunities to innovate, fully automate and bring the industry to the next level.
Need for 4th Industrial revolution:
The Fourth Industrial Revolution has the potential to raise global income levels and improve the quality of life for populations around the world. Technological innovation will also lead to a supply-side miracle, with long-term gains in efficiency and productivity. Transportation and communication costs will drop; logistics and global supply chains will become more effective; and the cost of trade will diminish; all of which will open new markets and drive economic growth leading you into a sustainable and profitable future.
Applications of Industry 4.0
Textile 4.0
Textile 4.0 is an interpretation and application of Industry Revolution 4.0 in the Textiles Technology and Textile Manufacturing sectors across the supply chain in Spinning, Weaving, Finishing and Garmenting. Due to the rising cost, high-end consumer, and the complex value chain, competitiveness of global manufacturing industry weakens and makes it imminent to upgrade.
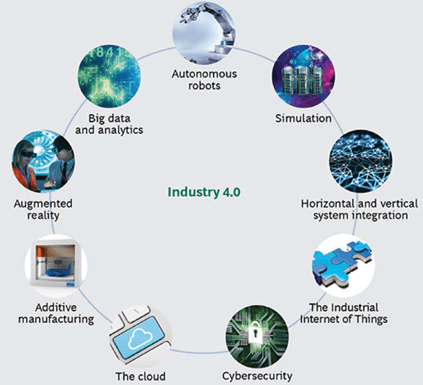
The world is at the threshold of a new industrial revolution characterized by Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, next-generation robotics, 3D printing, wearable’s, gentle engineering, nanotechnology, advanced materials, biotechnology and others. Industry 4.0 is the future of manufacturing technologies and is increasingly important trend in automation and data exchange. This enhanced technology, digital systems and automated processes will make it optimum for manufacturing of quality products. Industry 4.0 includes cyber- physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud computing and cognitive computing which creates what is being defined as a “Smart Factory”.
Smart manufacturing: It covers many different technologies. Some of the key technologies in the smart manufacturing movement include big data processing capabilities, industrial connectivity devices & services and advanced robotics.
Optimize logistics and supply chains: A connected supply chain can adjust and accommodate when new information is presented. If a weather delay ties up a shipment, a connected system can proactively adjust to that reality and modify manufacturing priorities.
Autonomous equipment and vehicles: There are shipping yards that are leveraging autonomous cranes and trucks to streamline operations as they accept shipping containers from the ships.
Robots: From picking products at a warehouse to getting them ready to ship, autonomous robots can quickly and safely support manufacturers.
3D printing: This technology has progressed from primarily being used for prototyping to actual production. Advancement in the use of metal additive manufacturing have opened up a lot of possibilities for production.
Internet of Things and the cloud: Not only does this help internal operations, but, through the use of the cloud environment where data is stored, equipment and operations can be optimized by leveraging the insights of others using the same equipment or to allow smaller enterprises access to technology they wouldn’t be able to on their own.
Artificial Intelligence: It is used by the textile companies for trend predictions and machine diagnosis and analyzing large chunk of data collected from manufacturing, purchase, marketing and logistics, etc.
Cyber-physical systems: From raw materials to product sales, digital tracking device is connected to each other according to standard protocols for data analysis, error forecast and self-configuring.
How will textile 4.0 help Indian Textile Industry?
The automation and artificial intelligence is gradually making a backdoor entry in the textile industry and in the coming years more and more textile production centres will become smart factories. Indian textile industry will have no choice but to catch up with the rest of the world by converting the production centres into smart factories in view of rising labour costs, increasing manufacturing and energy costs and wastages in the process. Only by riding on the wave of Textile 4.0, Indian manufacturing will become more competitive against major textile producing countries like China, Bangladesh and Srilanka. The Indian logistics sector is also rapidly adapting industry 4.0 and the supply chain of textile industry will get benefited due to the same in terms of proper production planning as well as fast movement of goods.
In view of the new challenges for the textile industry, it is necessary that the business leaders and the managers understand its implications and prepare a roadmap to successfully integrate the manufacturing, supply chain, marketing to achieve Textile 4.0 compliance. Textile 4.0 will also need a totally different skill set for the managers and the operators and a specialized training will be required for them to make them useful in the new era.
Challenges in implementation of Industry 4.0
Economic: High economic costs; Business model adaptation; Excessive investment.
Social: Privacy concerns, Surveillance and distrust, General reluctance to change by stakeholders. With adaption to Textile 4.0, the traditional jobs are likely to be lost making way for new generation of IT and technology oriented employees.
Conclusion
Industry is rebooting new digital age by adopting smart factory. The boom of global re-industrialization would make manufacturing more intense, competitive and the traditional model will be substituted for emerging model, which could be called integration of industrial chain better than an industrial revolution, and all participants in the production process will collaborate production in a new way. This manufacturing revolution will ultimately help in increasing productivity, improving economics resulting in fostering growth and changing the competitiveness of organizations.
References:
- https://www.textileassociationindia.org/upgrading-of-textile-manufacturing-based-on-industry-4-0/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industry_4.0 https://www.bcg.com/en-in/capabilities/operations/embracing-industry-4.0-rediscovering-growth.aspx
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2018/09/02/what-is-industry-4-0-heres-a-super-easy-explanation-for-anyone/#66565aab9788
- https://ategroup.com/news-and-media/TEXTILE-40–Is-the-Indian-Textile-industry-ready/ https://textile4zero.com/

Ms. Sampada Girish Surve
B.Sc. in Textiles & Apparel Designing
SVT college of Home Scinece
Intern at Textile Value Chain