The production of socks may not be considered a cutting-edge industry, but it encompasses a multitude of intricate procedures. Every step within the manufacturing process must work in harmony with one another to ensure both the desired level of quality and adherence to strict time constraints.
- PRODUCT CATEGORY: IMPULSE PURCHASE, LOW PRICE, FAST MOVING, Daily use
- PRODUCT BENEFITS AND PURPOSE: Covering of legs and hands from heat, cold, protection
- DURATION OF PRODUCT: Generally 1 to 10 washes
- MARKET SIZE: The global socks market size reached USD 44.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to surpass around USD 88.34 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 7.1% between 2023 to 2032. Market Overview: The socks market is a significant segment within the global apparel industry.
Over 400 million pairs of socks are sold in US stores alone each year (not counting discount outlets) The global socks market reached a valuation of US$ 56 billion at the end of 2023.
- MARKET: The airline, hospital, hotel, and Service industry needs hygiene and protection.
Highest Manufacturer in the World: China
Sock City, also known as the Datang district of Zhuji, China, is renowned for its exceptional contribution to the sock-manufacture industry. This district has gained significant recognition as one of the most productive cities for producing socks. It has been estimated that at one stage, the production from Datang accounted for nearly one-third of the global sock output. The region’s reputation for high-quality sock manufacturing has positioned China as a leading producer of socks worldwide.
Overview of Socks Manufacturing Process
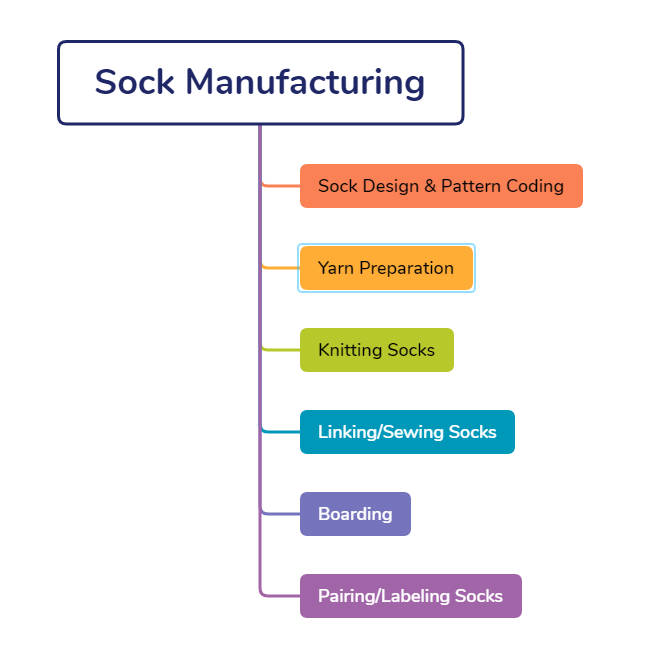
The whole sock manufacturing process involves many steps, and the coordination between these steps makes the whole process time-consuming. We will be primarily discussing a total of 7 steps after carefully organizing all the above-mentioned steps. Here is an overview of these steps:
- Pattern coding
- Yarn preparation
- Knitting socks
- Linking/Sewing socks
- Boarding
- Pairing&Labelling socks
1. Pattern coding
The sock designs are provided by the clients, but unfortunately, sock knitting machines lack the intelligence to directly interpret these designs. To overcome this challenge, a team of skilled coders, well-versed in both sock patterns and machine mechanisms, takes charge. Their role involves converting the vector designs into bitmap designs and subsequently creating codes that the knitting machines can comprehend. Each pixel within the bitmap design corresponds to a particular thread of a specific colour that will be seamlessly woven during the knitting process.
Different needles of knitting machines mean the widths of flat bitmap designs are different, 96N, 144N, 168N, and 200N of machines mean the widths are 96, 144, 168, and 200 pixels, respectively. The limit of thread count is the reason why socks can’t present gradients or detailed patterns.
2. Yarn Preparation
In the order details, we have confirmed 2 important things regarding yarn: Composition and Colors. Combed, compact yarn used for making socks with a count of 16 to 40’s.Generally, 6 kinds of fibres used in making yarns, that are :
- Cotton–The most common fibre used in socks from cotton plants which is breathable and strong ( Organic, Mercerised, Combed, Modal cotton). Manufacturers like NIVA Exports, Fiotex, Real Prince, Radheshyam Spinning.
- Polyester–Polyester, an artificial fibre, boasts the advantage of being both washable and highly wrinkle-resistant.
- Nylon–Produces more elasticity, nylon is stronger yet weightless.
- Spandex–More durable, and resistant to body oils, spandex can be stretched over 500% without breaking.
- Wool–Wool is the original easy-care fibre, naturally has wrinkle resistance, and breathes with your body. Types of wool used: Sheep, Goat, Alpaca, Rabbit
- Bamboo–Boasting a gentle touch softer than cotton, it offers a luxurious silk-like feel and remarkable long-lasting durability.
Basic 6 yarns in socks manufacturing, but a sock doesn’t contain them all common socks are usually made up of 3 yarns: 75% cotton, 22% polyester/nylon, plus 3% spandex.
The cost increases as we shift from sheep wool to rabbit wool, yet the calibre of wool relies on the length and thickness of fibres. Longer and finer fibres provide superior warmth and softness. Moreover, wool possesses innate anti-microbial properties, making it resistant to odours. Given its exceptional qualities, people are ready to invest more in acquiring woollen socks.
The best way of learning about sock yarn materials is by touching and sensing, even pics displayed you can’t tell which one is good or bad, but once you touch the fabric yourself, you can tell.
Process and Technology Companies for Making Yarn
- Blow Room: LMW , Truetzschler , Rieter, Saurer , many more
- Carding: LMW , Truetzschler , Rieter, Saurer , Bonino913, NSC , Recomatic, etc
- Comber: LMW, Rieter, Silver Star Agencies
- Speed Frame: Saurer, LMW
- Ring Frame: Prosper, Rieter, Toyota, Saurer
- Winder: Jwell, LohiaCorp, Rius, CEF ENGINEERING SRL, Polytex, SAHM Winding Solutions, Saurer
- YCP: Sieger, RBE, JOGSON, Bluemoon Machines
- Packing: SDP, Suriya Marketing, Sieger
3. Knitting socks
By utilizing programmed codes, multiple needles are employed to weave different threads into a sequence of interconnected loops. High-speed computerized sock knitting machines are capable of being easily programmed to manufacture a diverse range of socks. The incorporation of initial inline inspection ensures the prevention of errors such as incorrect length, trimming issues, and faulty interlocking, among others.
- KNITTING TECHNOLOGY USED: Circular Knitting
- CIRCULAR KNITTING: Companies making machines Mayer & Cie, Orizio, Tompkins, Santoni, Stoll, Karl Mayer, Terrot, Fukuhara, Shima Seiki
Sock Knitting Overview
Sock knitting machines are highly specialised circular knitting machines specific to the products made on them. These machines can use any type of yarn or fibre to produce hosiery and socks made of shape, size, and performance criteria. Socks knitting quality depends upon the following 4 factors:
- Machine Components
- Knitting Cylinder
- Knitting Needle Cycle
- Machine Types
4. Linking/Sewing socks
The art of knitting creates a tube shape, requiring the sewing process to connect individual toe sections. This linking step is typically accomplished using a speedy machine, although manual labour is sometimes employed, demanding substantial time investment. Skilled workers inspect and remove any faulty socks by hand, as each pair is sewn individually. This meticulous assessment forms the second stage of inline inspection.
Machinery Companies: Hefei HD Machinery, LMV, ROSSO
5. Boarding socks
The essence of the boarding process is to maintain the socks in optimal condition, preparing them for pairing and packing. Additionally, it effectively cleans and softens the socks, subjecting them to controlled steam, pressure, and temperature. Once boarded, the socks naturally air dry.
Machinery companies for this process: Prima-Tech, Autotex, Tabio
6. Pairing & Labelling Socks
This step marks the ultimate inspection phase where we carefully examine for any possible deviations in the socks. The pairing of left and right socks takes place before advancing them towards the stage of private labelling. As per your preference, you have the choice of utilizing hangtags or bands to effectively label your socks.
Leading Companies Operating in the Global Socks Industry:
- Adidas AG. Establishment: 1949
- ASICS Corporation. Establishment: 1977
- Drymax Technologies Inc. Establishment: 2011
- Hanesbrands Inc. Establishment: 1901.
- Implus Footcare LLC. Establishment: 1988
- Nike Inc. Establishment: 1964
- Puma SE. Establishment: 1948
- Renfro Brands.
- Bonjour: 1988
- Jasan Group: 1994
BEST SOCKS BRANDS IN INDIA
- Supersox
- Tommy Hilfiger
- Allen Solly
- Adidas
- Bonjour
- Jockey
- Heelium
- Puma
- SockSoho
- Nike
SWOT Analysis of the Industry:
The Socks industry, a vital segment of the textile and fashion sector, plays a crucial role in offering comfort and protection to the feet. As with any industry, the Socks industry is subject to an analysis of its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) to understand its market standing and potential for growth.
STRENGTHS:
- Diverse Material Options: The socks industry benefits from a wide range of material choices, allowing manufacturers to cater to different preferences and weather conditions.
- Growing Consumer Demand: Socks are a necessity for millions of people worldwide, ensuring a steady and consistent market demand.
- Versatility and Innovation: Manufacturers can introduce various designs, patterns, and functionalities, driving consumer interest and differentiation in the market.
- Low Manufacturing Costs: The production of socks often involves low-cost materials and efficient manufacturing processes, enabling affordable pricing and higher profit margins.
- Global Distribution Channels: Established distribution networks ensure extensive market reach and accessibility to consumers worldwide.
WEAKNESSES:
- Intense Market Competition: The socks industry faces fierce competition from numerous local and international brands, requiring constant innovation and marketing efforts.
- Low Brand Differentiation: With many similar products available, it can be challenging for brands to stand out and build distinct brand identities.
- Environmental Concerns: Some materials used in sock production, such as synthetic fibres, can have negative impacts on the environment, leading to potential consumer backlash.
OPPORTUNITIES:
- Growing Awareness of Sustainability: The increasing consumer focus on environmentally friendly products presents an opportunity for the socks industry to adopt more sustainable manufacturing practices and materials.
- Online Retail and E-commerce: The rise of online shopping platforms provides a convenient and accessible avenue for sock manufacturers to reach a global customer base.
- Seasonal Demand and Gifting: Special occasions and seasonal changes bring opportunities for marketing targeted collections, limited editions, and gift sets to stimulate sales.
THREATS:
- Economic Volatility: Economic downturns or recessions may affect consumer purchasing power and lead to decreased demand for non-essential items like socks.
- Counterfeit Products: Counterfeit socks flooding the market undermine the reputation and profitability of genuine brands.
- Price Competition: Price-sensitive consumers may opt for cheaper alternatives, putting pressure on profit margins for established brands.

