By Munish Tyagi
Global Textile Leader and Int`l Consultant to Technical
Textiles /Nonwovens
With 3rd highest and competitive availability of synthetic and MMF fibres and polymers like polyester, PP, nylons and viscose etc, India is now required to get in fast mode to up its global presence in Technical Textiles, with target of raising its technical textiles size to US$ 27 billion by 2026.
Shift to growing production of Technical Textiles
With reduced post covid retail demand for wearable textiles and apparels, and with increased availability of MMF and synthetic fibres of all types and including the recycled MMF fibres; there is increasing and expanding interest in nonwoven and technical textiles which will lead the global T&C demand at average 7-8% per annum vis a vis existing growth of 4-4.5%
Cotton and its erratic and unyielding prices continue to play havoc for exports of value adding textiles and apparels from many developing countries. With MMF fibres share touching 30-35% in developed economies, It’s the right time for their further growth and consumption vis a vis cotton textiles.
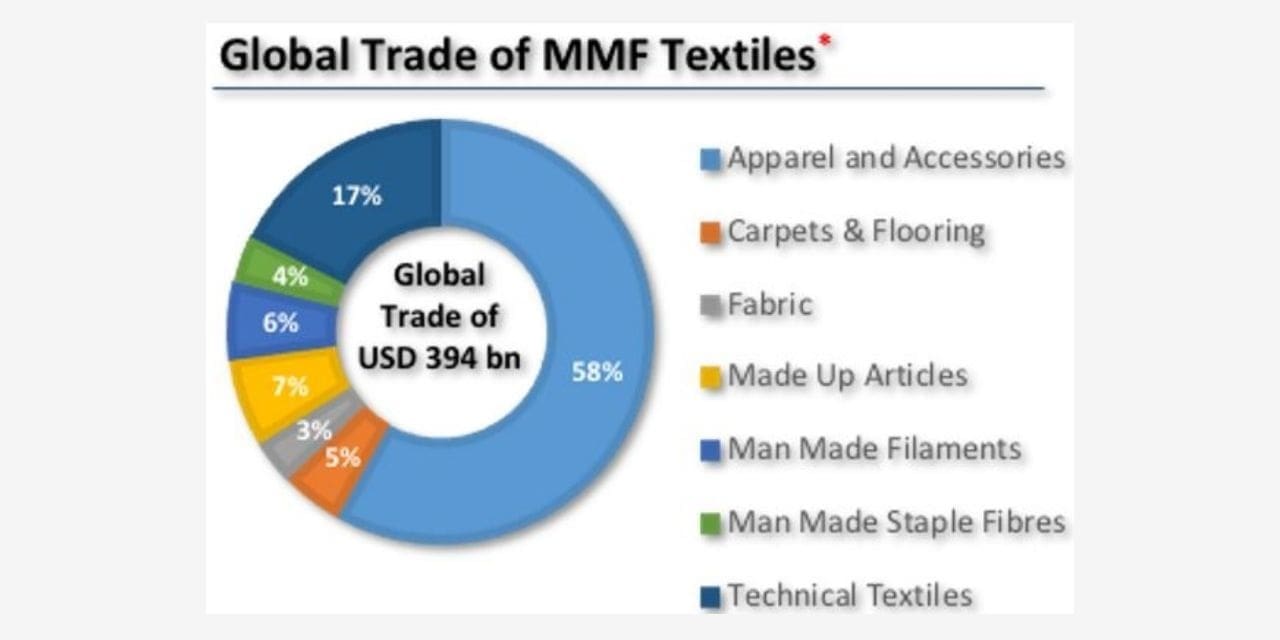
With this New paradigm shift and present-day scenario, this edition of Global Outlook focuses on India s planned initiatives to ramp up technical textile production and end use and also the exports to slot India once again amid top 3 global producers.
The current level of Technical Textiles industry in India
The global size of the technical textiles and nonwovens industry and its trade is presently at level of US$260 to 275 billion with a growth of 8%CAGR; which is almost double the growth rate of normal T&C sector at 4 to 4.5%. India’s share. In this fast growing and key textile sector is presently minimal at a total of US$ 20 billion turnover, which is less than 1% of the global size. This is not helping India upgrade its global supplier status.
China yet remains the leader, closely followed by Europe, and will be the main engine for driving India s MMF fibre consumption.
With 3rd highest and competitive availability of synthetic and MMF fibres and polymers like polyester, PP, nylons and viscose etc, India is now required to get in fast mode to up its global presence in Technical Textiles, with target of raising its technical textiles size to US$ 27 billion by 2026.
The Key drivers of this growth will be the new and increased focus on production of speciality industrial textiles to be end-used in hi-growth and strategic sectors like the medical textiles, geotechnical textiles,
Aerospace and high-altitude end use where India is very upbeat, the Indian Defence and civil infrastructure segments for creating high speed rail network, new ports, new airports and tunnels and road in high altitude areas like Kashmir, Ladakh and North East and also including a string of new highways, etc. It is now further endorsed that, with double the `demand `growth rate versus the traditional T&C textiles, the global textile recovery post Covid is to be led by this new industrial textile sector led by increased availability of MMF and synthetic fibres/filaments and growing industrial use of `speciality` and advanced materials based on new age fibres like Carbon, Aramide, Ceramic and glass fibre, etc.
INDIA’s 4 Aces, that is 4 most impactful new policies to help drive the production and use of technical textiles. The Indian Government is now ready to provide to the textile industry with its 4 new aces which will be the key engines of growth for technical textile sctor, as also for pushing India’s global T&C share:
a. The TTDS scheme, with an outlay of Rs. 160,000 million is being launched to replace the 25-yearold TUF scheme for incentivising the new investment in textile sector. However, the focus will be advanced technology and such indigenous machinery development capabilities.
b. The NTTM scheme [that’s is National Technical Textiles Mission spearheaded by Textile Ministry/ GOI] scheme, is being continued with a budget of Rs.10,000 million for the textile industry to venture into high tech projects in technical textiles arena.
c. The PLI or the production linked scheme is another new mega investment scheme to rope in large corporate and global investors into textile industry.The PLI scheme will bring in large output production and with focus on both MMF fibre use and manufacturing of technical textiles. Already more than 70 serious applications and project Intents have been registered.
d. The launch of the MITRA scheme for development and operations of large size or mega Textile Parks to attract large global investment into such world class `play n plug` manufacturing zones in different corners of the country and ideally placed close to the fibre production centres and seaports.
India’s competitive advantages v/s global competitions
To be able to enhance India’s textile sector size to US$100 billion plus by 2024, and slot itself with average of 8% share in global T&C/Tech textiles trade, India has to emerge as leading China +1 global supplier and lead from front using the competitive advantages such as;
Availability and access to all key raw materials and MMF fibres,
2. However, India has to make a strong thrust into develop and production of speciality fibres like carbon fibres, Aramides, ceramic, glass and other fibres with special focus on high tech textile end uses that are based on `sustainability` and green issues.
3. India does have the advantage of competitive wages, and yet needs to scale up for the production and new markets.
India yet needs to address the deficiency and critical gaps areas below India needs to actively pursue free-trade agreements
(FTAs) with major export destinations like the EU ,and the US to push apparel shipments amid increasing competition from fast growing rivals like Vietnam, Bangladesh, Turkey, Egypt, and Cambodia that enjoy tariff concessions, under liberal duty free trade agreements like GSP+ and TPT 11 and others.
India has traditionally enjoyed a comparative advantage in the cotton-based textile sector, including apparels, and they constitute a major chunk of India’s export basket. However, India’s shift to MMF textiles now has to be immediate and a serious call to enhance its share in the global T&C trade to more than 5% and also to take its rightful place as China+1.
Project No. Project Title Project Capacity
1 Export focussed YARN SPG MILLS,OF 25 K spdls,for BCI/ Organic yarns,for Knttg &wvg Approx..20 TPD
2 Cotton Yarn Mill with Ring and OE spg,withInhouse Knitting unit 15 to 20 TPD,
with 5TPD knttg.