Link: https://cen.acs.org/environment/green-chemistry/Transforming-textiles/100/i11
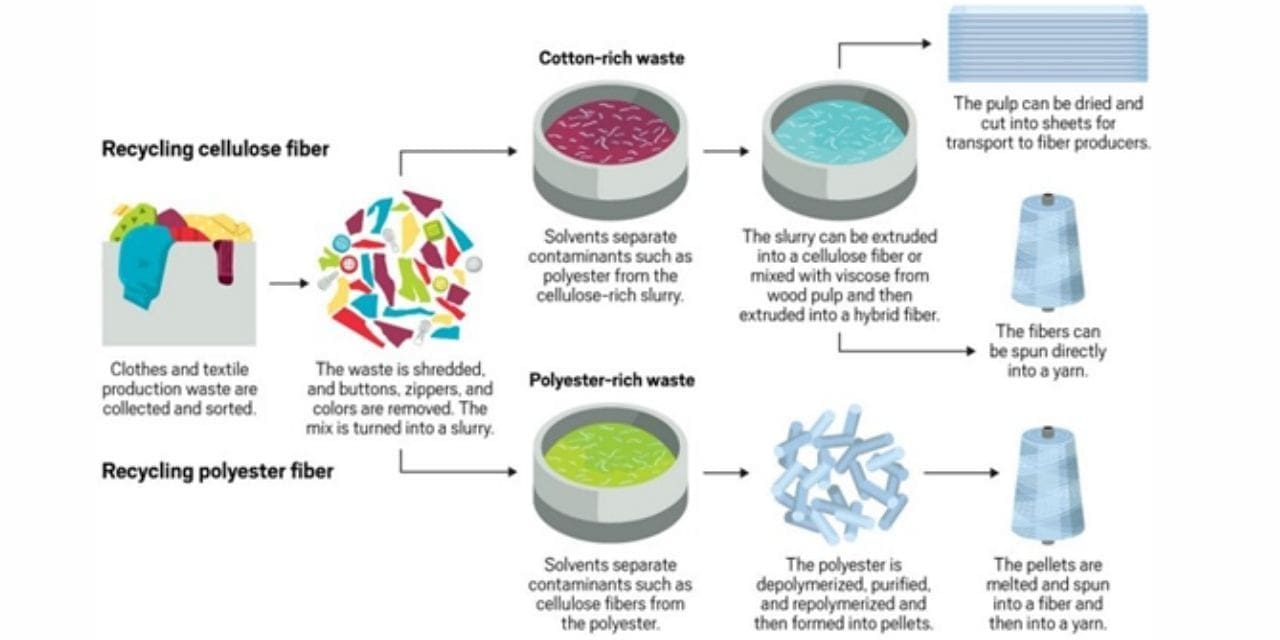
The material business, with its steadily developing natural impression, is shouting out for manageable innovations. An influx of new organizations is answering with substance based reusing innovations for every one of the fundamental strands, including cellulosics like cotton, and engineered materials like polyester and nylon.Mash from squander cotton used to make new cellulosic filaments.
Credit: Renewcell,Renewcell makes a dissolving mash from squander cotton that shapes the reason for new cellulosic filaments. Yet, no single organization yet has the total interaction to reuse all filaments. Also, not a solitary one of them are delivering financially practical measures of reused strands yet. Without a doubt, partners, including design organizations and waste gatherers, face bunch difficulties assuming they are to convey such advancements at a significant scale. A portion of the issues are specialized, for example, the inadmissibility of specific kinds of material waste to most reusing processes. An absence of satisfactory supplies of cellulosic material waste for reusing likewise lingers. On the off chance that the area’s key entertainers arrange, however, new reusing advances could assume a significant part in assisting the material business with cutting its ecological effect.
Customers all over the planet are purchasing clothing and different materials at such a scale that the area’s natural impression is currently the fourth biggest, after food, lodging, and transportation, as indicated by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, a UK think tank advancing the roundabout economy.
The world’s multibillion-dollar material industry produces 1.2 billion metric tons (t) of CO2 every year, more than the discharges from every global flight and sea transporting joined, as indicated by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation. Different effects incorporate the water and pesticides used to develop cotton, water contamination during fiber turning and coloring, and the arrival of microplastics into the seas from the family washing of pieces of clothing produced using engineered filaments.