Polylactic acid (PLA), also known as polylactide, is a revolutionary new material making waves in the textile industry. This bio-based fibre offers a sustainable alternative to traditional fabrics, boasting impressive properties that benefit both the environment and consumers.
From Plants to Fabric: The Production Process of PLA Fibres
 PLA is derived from renewable resources like corn, wheat, and sugar beet. Through a fermentation process, these starches are converted into lactic acid, the building block of PLA. The lactic acid then undergoes polymerization, a process that links the molecules together to form long chains, creating PLA. This eco-friendly approach sets PLA apart from conventional synthetic fibres, which rely on petroleum-based materials.
PLA is derived from renewable resources like corn, wheat, and sugar beet. Through a fermentation process, these starches are converted into lactic acid, the building block of PLA. The lactic acid then undergoes polymerization, a process that links the molecules together to form long chains, creating PLA. This eco-friendly approach sets PLA apart from conventional synthetic fibres, which rely on petroleum-based materials.
PLA: A Fibre with Strength and Sustainability
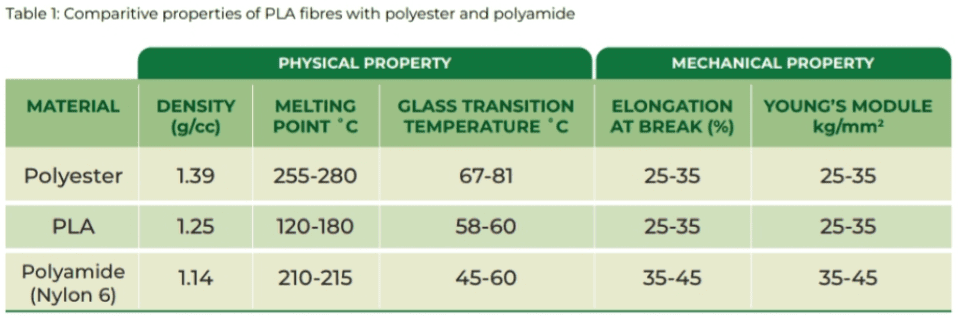
PLA fibres offer a unique combination of desirable characteristics. They possess good mechanical strength, elasticity, and the ability to be shaped using heat (thermoformability). These properties make PLA a versatile material suitable for various textile applications. Compared to traditional polyester and nylon, PLA offers a lighter weight, softer feel, and superior drape. Additionally, PLA fabrics are known for their excellent dimensional stability, meaning they retain their shape well.
Why Choose PLA Fabrics? A Look at Their Outstanding Performance
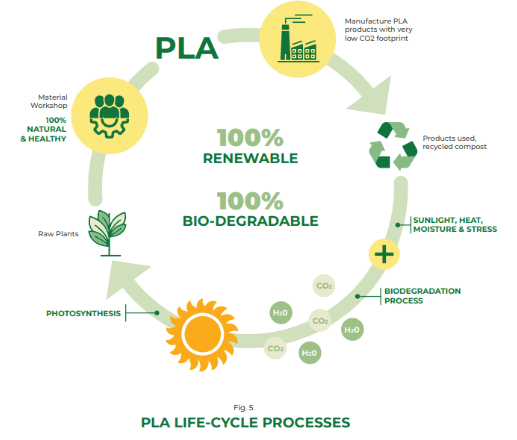
PLA truly shines in its eco-friendly performance. Unlike traditional fabrics, PLA breaks down completely into harmless water and carbon dioxide under specific composting conditions. This biodegradability makes PLA a significant contributor to reducing textile waste and its environmental impact. Furthermore, PLA boasts several health-conscious advantages. It is non-toxic and safe for human contact, making it ideal for sensitive skin. The lactic acid in PLA even exhibits natural antibacterial and anti-mite properties, further enhancing its hygienic qualities.
PLA’s Diverse Applications: From Clothing to Medical Supplies
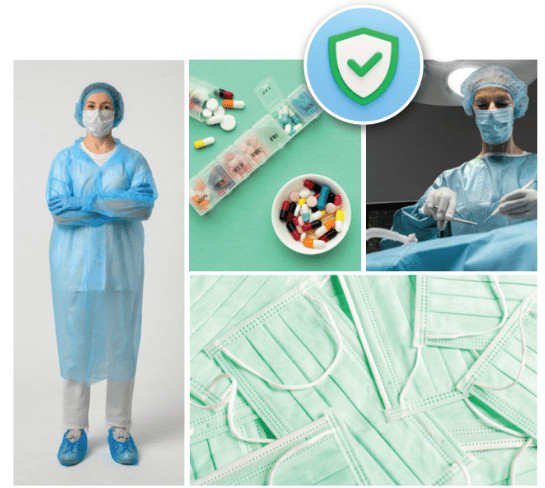
The versatility of PLA fibres translates into a wide range of applications. PLA fabrics are commonly used in clothing, sportswear, and bedding due to their comfort and breathability. Their inherent flame retardancy makes them suitable for household items like curtains and carpets. PLA also finds use in the medical field, with applications in surgical sutures, drug delivery systems, and medical textiles.
 Transforming PLA into Fabrics: Spinning and Weaving
Transforming PLA into Fabrics: Spinning and Weaving
PLA fibres can be processed using various spinning techniques, including ring spinning and vortex spinning. These methods allow PLA to be spun alone or blended with other natural or synthetic fibres for added functionality. The resulting PLA yarns can be used to create both knitted and woven fabrics. After dyeing and finishing at lower temperatures with dispersed dyes, PLA fabrics can be transformed into a vast array of textile products.
Beyond Clothing: PLA’s Use in Non-Woven Fabrics
PLA’s applications extend beyond traditional fabrics. Non-woven fabrics made from PLA fibres are becoming increasingly popular. These fabrics are produced through processes like needle punching and hot air bonding. PLA nonwovens find use in disposable products like diapers, wipes, and masks, further showcasing the diverse applications of this sustainable material.
PLA as a Filling Material: Comfort and Warmth
 PLA fibres can be directly used as filling materials for pillows, cushions, and plush toys, offering a soft and comfortable feel. Additionally, PLA can be incorporated into bedding products like quilts and pillows for enhanced warmth and insulation.
PLA fibres can be directly used as filling materials for pillows, cushions, and plush toys, offering a soft and comfortable feel. Additionally, PLA can be incorporated into bedding products like quilts and pillows for enhanced warmth and insulation.
The Future of Textiles: A Sustainable Outlook with PLA
Polylactic acid fibres represent a significant step towards a more sustainable textile industry. Their eco-friendly production, biodegradability, and diverse applications make PLA a promising alternative to traditional fabrics. As research and development continue, PLA is poised to play an even greater role in shaping the future of sustainable textiles.


