CLASSICAL GREEK MYTHOLOGY AND RELIGION
• The influence of the Ancient Greeks are still felt by us today. The major impact in our livestoday are in the arts, in philosophy, and in science, math, literature and politics.
• The Ancient Greeks believed in many different gods and goddesses. The Greeks believedthat these gods andgoddesses controlled everything in their lives and the environment. There was a god for every aspect of their lives.
• Zeus (Roman name Jupiter) Married to Hera. Zeus is lord of the sky, the rain god
• Poseidon Brother of Zeus. The God of the sea
• Hades Brother of Zeus. God of the underworld, ruling over the dead.
• Aphrodite Wife of Hephaestus. Goddess of love, desire and beauty.
• Apollo is the god of music, playing a golden lyre. The Archer, far shooting with a silver bow. The god of healingwho taught man medicine. The god of light. The god of truth,
• Artemis Daughter of Zeus and Leto. Her twin brother is Apollo Artemis is the huntsman of the gods
• Athena Goddess of the city, handicrafts, and agriculture
SOCIETY
• Men
Men had a much better life in Ancient Greece than women. Only men could be full citizens. Onlymen made the important decisions. Normally, only men fought in armies, tookpart in sports andmet in public.
• Women
Spartan women were taught reading and writing and skills to protect themselves in battle. They had more freedom than women and girls living in Athens. As well as looking after the house making clothes. Women in Athens were taught skills they would need to run a home such as cooking and weaving. They were expected to look after the home, make the clothes, and bear children.
- Slaves
Only in the poorest homes were women expected to carry out all the duties by herself. Mosthomes had female slaves who cooked cleaned and collected fresh water every day.There were also male slaves. Their responsibilities included protecting the home andtutoringmale children.
CULTURE, THEATRE, ART AND PHILOSOPHY
Almost every Greek city had a theatre beart of many religious festivals. TheGreeks enjoyed singing and dancing. The theatres were built on hillsides in the open airand could often hold more than 18,000 spectators. The theatres were open air and built in a semicircular. In the centre of the theatre was a circular dancing floor (orchestr). The stage was a raised area within this circle. All the actors were men. They wore large masks that exaggerated facialfeatures and emotions. The mouth hole was largeto help amplify the voices. Greek plays were either comedies or tragedies. Plays were either spoken or sung in rhyme.
PHILOSOPH Y
Greece is the mother of the western philosophy with the most influential philosophers:
• Plato (c.429-327 BC) – He was a brilliant student of Socratesand later carried on his work. He gathered Socrates’ ideas andwrote them down in a book. Plato founded the world’s firstuniversity. He wrote down his teachings and peoples all over the world, even today, study the Greek philosophers
• Aristotle (382-322 BC) – discovered many things in scienceand biology. He wrote books about physics,poetry, zoology, biology, politics, governments, and more. His father was the personal physician of the King of Macedonia. When Aristotle turned 17, he went to Athens to study with Plato.
• Aristotle has an influence on design and art: he defines art and the principles of design.
• Parmenides – watched an eclipse of the Moon in about 470BC, and noticed that the Earth’s shadow was curved. Heworked out that if the shadow was curved, then the Earth must be round.
• Archimedes – was a mathematician and an engineer. He designed a machine, called the Archimedean screw, whichcould make water flow uphill. His design has been used for almost 2,000 years, to take water from rivers to the fields. Archimedes was able to tell fool’s gold from real gold
• Pythagoras – was a mathematician who fond out about Pythagoras’ theorem on right angled triangles.
• Alexander the Great
Alexander the Great was born in 356 B.C. in Pella, Macedonia, the son of Philip of Macedon, who was an excellent general and organizer. He was called ‘the Great’because he conquered more lands than anyone before himand became the overall ruler of Greece
Source of information
• Ceramic vases, statues
Constituted for the archaeologist and thehistorian the main sourcefor understanding thestyle, the costumes, hairstyle, habits of theGrecians

MINOAN CULTURE 3000 – 1600 BC
Generally, when we speak about Greeks we speak about the classical Greeks from 7 th centuryonwards,with the famous people like Plato, Aristophanes, Sophocles etc. But long time before them, in a small island name Crete, in Greece, was an incredible civilisation and clothing.
The Minoans, who lived on the Greek island of Crete between 3000 and 1600B.C.E. had
a verycomplex culture, more advanced than many of the societies that followed it. This
complexity is shown in the artistically designed and skilfully made clothing they wore.
Minoans wore a variety of complex garments thatwere sewn together in very much the
same waythat modern garments are made. Minoans sewed skirts andblouses that were
shaped to thebody of the wearer

MEN
• Ancient Minoan men wore only loincloths, whichwere small pieces of fabric wrapped around thewaist to cover the genitals. However, even these small garments were madewith much attention to detail.
Loincloths were made from a wide variety ofmaterials, such as linen, leather, or wool, and decorated with bright colours and patterns. Many had a decorative pagne or sheath that covered and protected the penis,and somehadlong aprons in the front and back with tassels or fringe. While early Minoan men usually went barechested,in the later years of theMinoanCivilization men often wore simple tunics and longrobes

WOMEN
The first modern scholars to studyCrete were astonished by thedesign of the women’s costume, including blouses and skirts that closely resembled modern women’s clothing. Minoan women wore skirts thatflared out from the waist in a bell shape, with many decorations attached to the cloth. Later designs were made fromStrips of fabric, sewn in ways thatcreated rows of ruffles from waistto ankle.

Minoans women
Women also wore close-fitting blouses that were cut low in thefront to expose the breasts. A tiny waist was prized, and bothmen and women wore tight beltsmade of metal, which held their waists in some historians believe that these belts must have been worn since early childhood, forcing the waistto stop growing.

MINOANS
The snake Goddess is either a statue of a snakegoddess, or a priestess of the snakegoddess, this was found at Knossos. she is wearing is a sewn garment. Theskirt she is wearing may have hadframework underneath it to supportthe bell shape of it. The blouse she iswearing is also sewn and then cutrather low. There was also an item ofclothing that might be worn under theblouse, which was similar to thecorsets that were worn from aroundthe Renaissance period onwards.

CLASSICAL GREEKS: CLOTHING INTRODUCTION 700 – 146 BC
The Greeks wore light, looseclothes as the weather was hotfor most of the year. Long piecesof colourful fabric were used to make the Greek clothes.

Ancient Greece 700 – 146 BC
1. CHITON worn by both men and women
2. Chiton was fasten with a broche called FIBULAE
3. PEPLOS, an earlier form ofchiton, was worn over the chiton ( in the later Greek empire)
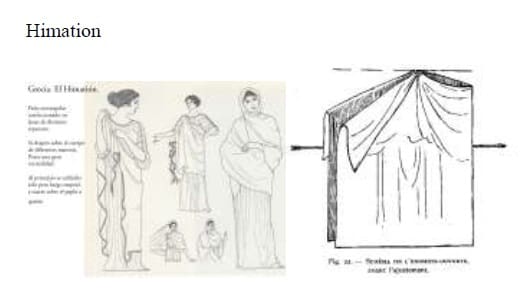
4. HIMATION worn over the chiton
5. CHLAMYS was worn by soldiers, instead of Chiton

The clothing would serve manypurposes such as garments, blanket Both men and women sharedthe same types of clothing but lengths and style varied Fabric was brightly coloured and dyed and decorated.
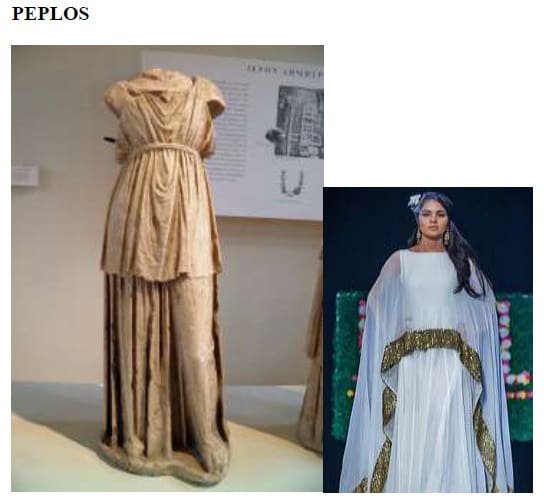
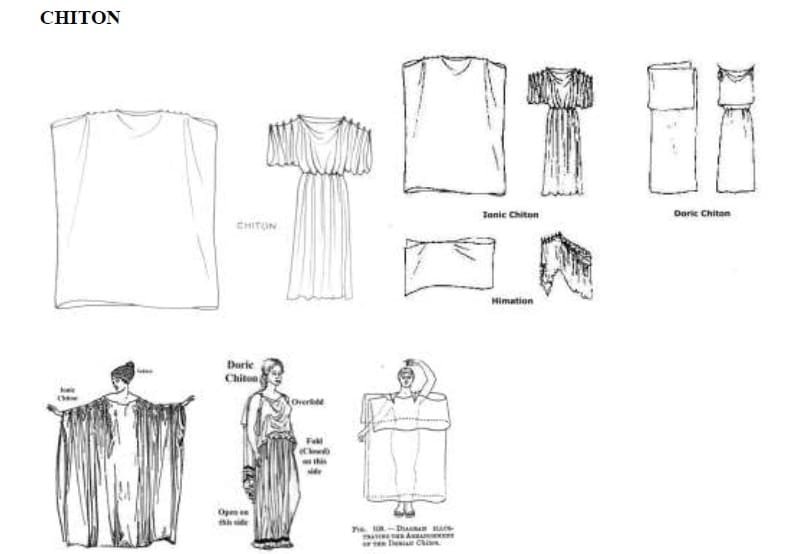


FABRIC AND ACCESSORIES
• Wool and linen were usedmainly. Cotton and silk were used occasionally. Colours like white, reddish brown, bright orange, red, emerald green, red purple, dark green. White and red were worn bypoor people.
All other colours were worn by the rich, withgarment with borders.

FOOTWEAR
• Accessories were leather sandals, and walking sticks. Footwear like strip sandals and for soldiers boot with strips. Made from cattle hide, animal skin and leather thick sole for war. Sandals were worn by bothgenders with various types and fastener stalaria
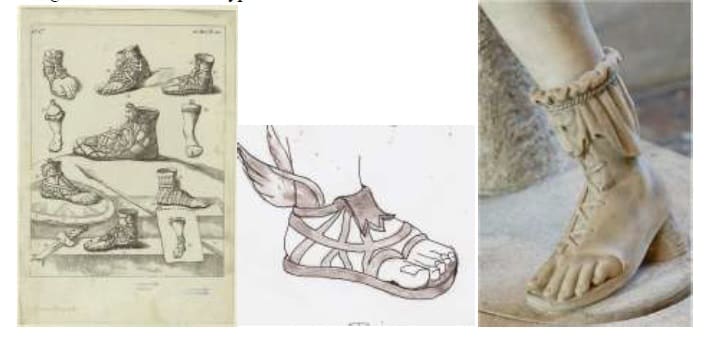

SHOES
• Embeds: enclosed boots with feltand fur outer lining
• Krepis: outdoor boots for rocky terrainused by military
• Cothurness: used in theatre
• Buskin: used by soldiers, hunters, actors. In cloth or leather with closedlaces
• Phacaseim: priests, countrymen, philosophers
• Talaria: mythological winged sandals
• Carbatine: single piece of raw hidewith a thong

HAIRSTYLE
• Men had beards and the hairwas curled around the face, to frame the face, or Men had long hair and they tied it with a ruban. Beard wears the symbol of strength, wisdom and manliness. Beard could only get cut if mourning. Women made complicated hairstyles, breads, ringlets, topknots and chignons. They liked to have long hair. Hair were bleached also or with airlines.Brunette type liked to have golden hair and they could achieve by using vinegar in the sun or yellow flower dye. They were already using olive oil for
moistening their hair. Women were using also fresh flowers, ribbons, tiaras, gold and silver hairpins, and head dresses. They would cut their hair for morning. They liked to have long hair. Hair was bleached also or with airlines. They liked to have long hair Hair were bleached also or with airlines. Brunette type liked to have golden hair and they could achieve by using vinegar in the sun or yellow flower dye. They were already using olive oil for moistening their hair. Women were using also fresh flowers, ribbons, tiaras, gold and silver hairpins, and head dresses. They would cut their hair for morning



MAKE UP AND COSMETICS
Kosmetikosis the Greek term for cosmetics meaning sins of tranquillity, harmony, and order. Cosmos meaning order in ancient Greek. Most items used to make cosmetics were natural Pale skin was in fashion but harmfulproducts were used to achieve it. White lead was mixed with water andapplied on their face, neck, shouldersand arms to create a smooth paleskin.

MAKE UP
Charcoal was used for the eyes, eye shadow, liner. Red on the lips came from the red ochre. Henna was painted on nails and hands. Using mot of perfumes. Dark powder was dusted over theeyebrows and red powder on thelips. For a time, even the connected eyebrows (the unborn) was invogue

JEWELRY
Both men and women were wearing jewellery, gold chains, pendants, rings, bracelets, and jewels pins.

Fashion of today inspired by GREECE/ LANVIN

MODERN FASHION INSPIRED BY GREECE

REFERENCE:
Study done by Mrs. Diana linda
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greek_dress
https://world4.eu/the-ancient-greek-costume/
https://people.howstuffworks.com/culture-traditions/national-traditions/greektradition2.
htm
http://www.fashionencyclopedia.com/fashion_costume_culture/The-Ancient-World-
Greece/Greek-Clothing.html
