Dr. P.P. Raichurkar and Ranjit Turukmane
Centre for Textile Functions, SVKM’S NMIMS, MPSTME, Shirpur, Dhule (M.S)
Abstract
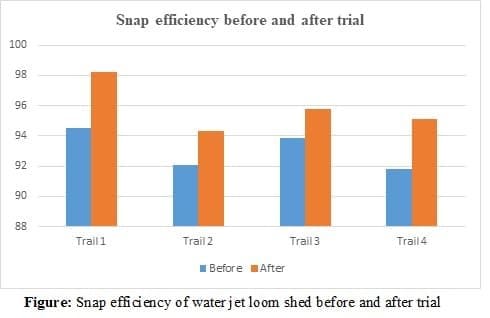
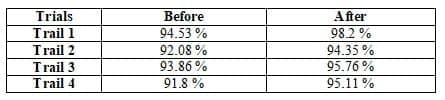
Water jet looms are specially used for weaving of synthetic yarns. Water jet looms are widely used in woven fabric manufacturing because of their unique parameters such as low noise, low energy consumption, high weft insertion speed and less maintenance. Sometimes several poor material handling practices and technical errors lead to the loss of productivity and efficiency of the loom shed especially in case of for synthetic fabric production. In this research we have focused on the normal practices followed by the technicality for improving water jet loom shed efficiency by snap study technique. The observation were made on real time basis and actual data collected. There we have taken a snap rounds per 2 hours a shift and it was found that after correction and remedial actions the loom shed efficiency was increased successfully such as 98.2 % from 94.53%.
Key words: Efficiency, Maintenance, Synthetic yarns, Water jet loom
1. Introduction
Productivity is a burning issue in the textile industry. Where loom shed efficiency is very important and can turn in to profit of the textile mills. If there is a small increase in productivity of a loom shed will result in a considerable reduction in manufacturing cost. The productivity of loom will increase the fabric value and result in profitability. This will help to make an additional fabric available in the store of industry. For medium average mills, an increase of 2% in the loom shed productivity can increase the annual cash inflow by Rs.6lakh or more. In various man-made weaving, several parameters were considered for enhancing productivity levels such as yarn quality, quality of yarn preparation, loom setting and atmospheric conditions in the department.
The simplest measure of machine productivity in weaving is the length of the cloth produced per unit time say per shift of 8 to 12 hours. The loom efficiency depend on the stoppage rate, time to taken to mend a stop loom allocation and the percent time the weaver spends on restarting a loom after a stoppage therefore, beside minimizing the stoppage rate, optimum loom allocation, loom setting and atmospheric condition in the loom shed.
The simplest measure of machine productivity in weaving is the length of the cloth produced per unit time say per shift 8 hrs the loom efficiency depends on the stoppage rate, time to taken to mend a stop loom allocation and the percent time the weaver spends on restarting a loom after a stoppage, therefore, besides minimizing the stoppage rate, optimum loom allocation. All the factors which influence the loom shed efficiency are categorized into three main streams viz. Technical, human and organizational.
Various factors which affect the loom shed efficiency can be conveniently grouped in three major categories
1) Technical
2) Human
3) Organizational
Such a classification will facilitate taking the corrective action needed for improving loom efficiency these four categories their component causes and those controlled factors which have been commonly found to need attention for improving efficiency. The conformity of the quality of yarn to norms has to be ensured by the spinning department. Further the process control programmed in the preparatory section has to ensure good quality of preparation. It then remains to identify the cause and their contribution to the loss machine efficiency. A suitable format for recording loom performance in terms of end breaks and other stops is now required. Such a record of loom performance will be helpful in controlling productivity on loom in more than one ways firstly a regular record of end breaks bring out need for any technological adjustment. Snap study technique is the key for analysis of the causes and their contribution in the efficiency loss.
2. Material and Methods
2.1 Yarn Quality requirement:
The warp breakage rate is relatively insensitive in strength, but with a reduction in strength below a critical level, the warp breakage rate increase rapidly. Quality of the yarn is primary source influence end breaks. A weak, fuzzy and non-uniform yarn will break very often. The requirement is strong, smooth, uniform yarn with high elongation at break to withstand the weaving stresses better, consequently improving the weavabality of yarn.
2.2 Technical yarn details
1. Standard average denier
– 77.60
– 77.80
– 76.76
– 77.24
2. Elongation – 15.27%
3. Tenacity – 3.85 (Grams/denier)
2.3 Quality of weaving preparatory process
The warp breakage rate is governed by the yarn quality as well as quality of warping. Good quality yarn is not itself capable for weaving without sizing. In warping and sizing process emphasis is given on quality of the process rather than productivity.
In warping should aim at minimizing end breakage rate production of satisfactory beam that will unwind well during sizing. The stoppages of the machine due to end break are likely to deteriorate the quality of the beam. End breaks in warping can be minimized by different method.
1) Control of tension in the yarn.
2) Satisfactory maintenance of that setting and mechanical condition of the machine that affects yarn tension.
3) Minimizing the defect on package produced at winding.
4) A regular check on the end breakage rate for comparison with the norm.
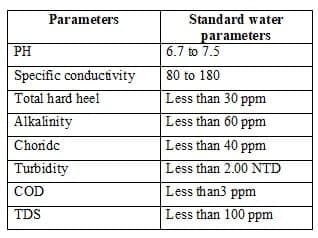
2.4 Standard parameters in water jet loom
Water requirement per machine
Water = pressure
Water pressure in 1 machine
1 min = 6 liter
6×60= 3.60 liter
6×60×24=8440 litr per m/c 24 hrs
3. Result and discussion
As the word ‘snap’ indicate recording of the incidence should be spontaneous the person who takes snap round should not anticipate an incipient stoppages, should he wait for it to occur as he goes round. A suitable format for listing causes of stoppages during snap rounds in a loom shed. When sufficient round is taken data from all the reading are pooled together the total number of looms found stopped during the round expressed as a percentage of all the looms inspected all during all the round is good measure of the loss of loom efficiency. Quality of yarn is primary source influencing end breaks given a quality of yarn the end breaks during weaving are increased by,
Preparatory deficiency such as unlearned yarn fault.
Fault loom setting.
Defective loom parts and accessories.
Unsatisfactory atmospheric condition in loom shed.
The warp stop due to warp fault such as slack ends, sticky ends, crossed ends; missing ends, etc. are mostly due to preparatory deficiencies. Most of the loom setting that influences the end breakages rate in the loom shed need to be corrected at the time of beam change once set these setting is expected to remain correct at least for the duration of one beam.
The snap study was taken for every 2 hours per shift. It was found that there were several factors responsible for efficiency loss. Earlier the warp and weft breakage were found to more due to improper loom setting Viz. high warp tension, improper shed height, high beating force and poor material handling practices. It was found that the optimized loom settings and proper material handling helps to increase the loom shed efficiency. Whenever one operative had two or more machine under his care, each machine is liable to stop in a random manner and requiring attention before restarting, a loss in machine efficiency takes place due to interference. The interference arises from the fact that the machine is waiting for operator’s attention that is busy for attending another loom.
Practices: To given proper training for weaver.
Supervision: Weaver should be done proper supervision or patrolling for given loom.
Work load: To make a proper allocation that is man to machine. E.g. six loom per weaver.
Following are to be considered as a Benefits of yarn breakages reduction
1) Cost Reduction:
When we reduce the yarn breakages the loom, the cost is also reduced. If there are stoppages at the loom because of any yarn breakages problem than it will be repaired and some cost will increase in this manners. When we entangled this problem which cause the loom to stop, the cost automatically goes down.
2) Man Power:
After resolving the problem which cause loom to stop man power will also be reduced. If there is problem of yarn breakage constantly at the loom than a person will be required to handle this situation, and when we solve this problem than there will be no need of person constantly at the loom.
3) Effect on Production:
When there is problem of yarn breakage or problem in the mechanical part of loom, the loom will stop to work. In this way the productivity of loom will be affected and when we solve these problems production will also be increased.
4) Quality of Fabric:
Yarn breakages on the loom also affect the quality of fabric. When there is constant breakage of yarn and there is definite knotting for this problem. It will damage the quality of fabric. When these problems are solved the quality will also be improved.
5) Wastages of Yarn:
Constant yarn breakages on loom due to different problems also cause the wastage of yarn .This problem will also be solved by reducing the yarn breakages on the loom.
6) Loom Efficiency:
When the yarn breakages occur because the looms to stop are reduced the loom shut down will also be reduced. This will affect the efficiency of loom and it will increase.
7) Reduction of Start Mark:
Start Mark is a sign which comes on the surface of the fabric when a loom is restarted after a shut down. When there is any problem due to which loom gets off again and again it will leave a “Start Mark” at the surface of fabric and it effect the fabric very badly. After solving the problem this effect will also be reduced and a good quality fabric may obtain.
- Conclusion
From the above trials it have been concluded that, the optimum settings and proper material handling practices and utilization of other factors leads to increases the loom shed efficiency. Following corrective actions were done during after trial sessions to reduce considerable production loss and efficiency of the loom,
- Time attend to breaks is can be reduced by set time to standards.
- Telling the worker to attend the break quickly.
- To gives the optimum allocation to weaver.
From correct work practices we can reduce the attend the mending time
- 13min. 41sec.
- 9min.5sec.
- 9min.10sec.
- 16min.34sec.
All these practices increased efficiency in following manner
Table: Snap efficiency of water jet loom shed before and after trial
- References
[1] Hasanbeigi A, Price L. A technical review of emerging technologies for energy and water efficiency and pollution reduction in the textile industry. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2015 May 15;95:30-44.
[2] PK Hari and BK Behera; “Developments in weaving machines”,indian journal of fiber & textile research,vol 19,september 1994.pp 172- 176.
[3] Maniya k.d; multi-attribute evaluation of water jet weaving machine using analytical hierarchy process.jtatm journal of textile and apparel technology and management.volume6,issue 4,fall 2010.
[4] N Gokarneshan,N Jegadeesan & P Dhanapal.Recent; Innovation in loom shedding mechanisms, Indian journal of fiber &textile research.Vol 35,March 2010,pp 85-94.
[5[ Seyam AM. Weaving Technology: Advances and Challenges II. Journal of Textile and Apparel, Technology and Management. 2003;3.