This article focuses on importance of water audits, commercial impact of the same on profitable manufacturing and measures on reducing the water footprint on various types of industries. The water balance sheet of any industry gives you insight of current situation and roadmap for future water conservation action plan.
========================================================
As the financial year end is close by, every business is busy in financial closure. But have you ever made your water resource balance sheet? It’s high time for the same too.
Water is a precious natural national resource with almost fixed quantum of availability. With continuous growth in country’s population, per capita availability of utilizable water is going down, whereas with ever-rising standard of living of people, all around rapid industrialization and urbanization, demand of fresh water is going up continuously. Unabated discharge of industrial effluents into water bodies is further aggravating the situation of scarcity of water of Acceptable quality. In spite of the fact that fresh water is rapidly becoming scarce it is continued to be used wastefully.
Rapid industrialization and urbanization coupled with continuous decline in per capita water availability is putting a lot of pressure on the available water resources in the country. Hence, it is important to understand the dynamics behind water audit and its impact on profitability of production.
What Is Water Used For?
Water is used by commercial, institutional and industrial customers for five primary purposes:
- Indoor domestic use (rest rooms, kitchens, and laundries)
- cooling and heating
- landscape irrigation
- processing of materials
- As an ingredient
Examples of water uses in commercial and institutional facilities
- Indoor (Domestic) Water
- Kitchens, cafeterias, staff rooms –
- Faucets
- Distilled/drinking water
- Ice machines
- Dishwashers
- Garbage disposals
- Food preparation
- Restrooms and showers
- Faucets
- Toilets and urinals
- Showers
- Laundry – washing machines
- Sanitation
- Facility cleaning
- Sterilization/autoclaves
- Equipment washing
- Dust control
- Container washing
- Processes – photographic and x-ray processing, silk screening, dry cleaning, printing, etc.
- Cooling and Heating
- Cooling towers/evaporative
- coolers Boilers and steam systems Once-through cooling
- Air conditioners
- Air compressors
- Hydraulic equipment
- Degreasers
- Rectifiers
- Vacuum pumps
- Kitchens, cafeterias, staff rooms –
- Outdoor Water Use
- Irrigation
- Pools and spas
- Decorative water features
While establishing any new industry, water and energy are 2 most important factors considered from any factory and processing industry operation point of view. And, water audits can play very important role in the assessment. Water audits are effective methods to account for all water usage within a facility in order to identify opportunities to improve water use efficiency. Benefits from implementation of water audit may include lower utility costs, energy savings, and reduced process costs.
What is Water Conservation?
Water conservation, also known as water use efficiency, is an integral part of water supply planning and water resource management. Water conservation is defined as the beneficial reduction in water use, waste, and loss. Water conservation is becoming a viable alternative and complement to developing new water supplies. While short-term water restrictions imposed during a water shortage can temporarily relieve pressure on water sources, lasting water conservation involves a combination of retrofits, new water saving appliances, maintenance of infrastructure, and a collective water conservation ethic focused on resource use, allocation, and protection.
What is water audit?
A water audit is an on-site survey and assessment of water-using hardware, fixtures, equipment, landscaping, and management practices to determine the efficiency of water use and to develop recommendations for improving water-use efficiency. In simple words, a water audit is a systematic review of a site that identifies the quantities and characteristics of all the water uses. The site may vary from a public water utility, facility (institutional or commercial properties like malls, office, schools etc.) or a household. The overall objective of conducting a water audit is to identify opportunities to make system or building water use more efficient.
Facility water audits include –
- accurate measurement of all water entering the facility
- the inventory and calculation of all on-site water uses and any unused water sources or waste streams that may be available
- calculation of water related costs
- And identification of potential water efficiency measures.
The information from the water audit forms the basis for a comprehensive conservation program to implement specific water saving measures throughout the facility. The conservation program may consist of one or more projects in different areas of the facility.
Estimation of Wastewater Generation & action plan to reduce the generation
It is difficult to assess wastewater generation from industries on the basis of average generation of wastewater per product unit, mainly due to large variations in volume of wastewater generation per product unit. However owing to various constraints, present estimation of industrial wastewater is based on average generation of wastewater per unit product.
The volume of wastewater and concentration of various pollutants in industrial discharge vary depending on manufacturing processes and other factors such as housekeeping, reuse, technology, etc. Even for a given manufacturing process, the amount of wastewater generation depends on several factors, for instance:
- Housekeeping practices – Housekeeping practices refer to simple measures such as arresting leaks from pipes, stopping of unnecessary overflows from the vessels, improving material handling procedures to reduce losses. Poor housekeeping results in significant generation of wastewater.
- Extent of process control – Process control includes setting up of process parameters to optimum levels leading to best possible yields and minimum wastage of water. Product quality requirements refer to commercial specifications, which may vary depending on market.
- Product quality – Product quality requirements including packaging – Achieving better quality generally require additional processing and improved raw materials and thus may generate more wastes.
- Management systems & initiatives – The management systems include entire sequence of raw material processing, technology and production of finished product.
The emphasis on curtailing wastage in handling and improvement in operation processes through better management can lead to minimization of wastes.
The results from water audits should be used for leak detection, minimization of wastewater generated, implementation of water conservation plans such as Rainwater harvesting and watershed management, wastewater recycling, zero liquid discharge policy and so on.
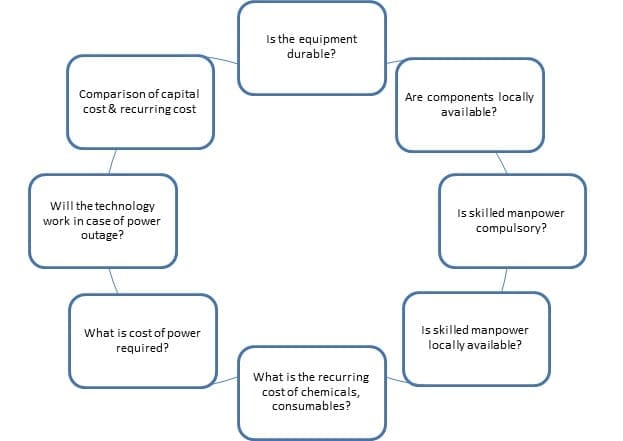
Selection of Right kind of technology for wastewater Treatment & Reuse:-
It is very important to select right kind of technology for wastewater processing. Generally emphasis is given only on capital cost and operation maintenance, recurring costs are overlooked. Hence, it is important to answer following questions before narrowing down on choice of technology.
Need for implementation of long term sustainable measures like Rainwater Harvesting
India has enough rainwater available throughout the year. It is question of utilizing the same. As the rainwater is purest source of fresh water, it is important to have long term vision about business sustainability and not just short term vision of payback criteria. As availability of water can largely hamper the production, it must be considered while investing in other short term options like purchasing water from outside temporary resources.
Small Industry Wise Tips
It is a typical mindset of the industry that profits are generally made by not treating wastewater properly and hence saving on the treatment cost. But as the “polluters pay” policy is becoming effective day by day, there is requirement of paradigm shift from mindset of “profit in pollution” to “profit from water recovery” and “resource recovery from waste”.
========================================================
©Chitralekha Vaidya
22/02/2017